| Issue |
A&A
Volume 434, Number 3, May II 2005
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 819 - 825 | |
| Section | Cosmology (including clusters of galaxies) | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20042034 | |
| Published online | 18 April 2005 | |
Molecular gas in a z  triply-imaged, sub-mJy
submillimetre galaxy typical of the cosmic far-infrared background
triply-imaged, sub-mJy
submillimetre galaxy typical of the cosmic far-infrared background
1
Observatoire Midi-Pyrénées, CNRS-UMR5572, 14 avenue E. Belin, 31400 Toulouse, France e-mail: jean-paul.kneib@oamp.fr
2
Caltech-Astronomy, MC105-24, Pasadena, CA 91125, USA
3
OAMP, Laboratoire d'Astrophysique de Marseille, traverse du Siphon, 13012 Marseille, France
4
IRAM, 300 rue de la Piscine, 38640 Saint Martin d'Hères, France
5
Institute for Computational Cosmology, University of Durham, South Road, Durham DH1 3LE, UK
6
Leiden Observatory, PO Box 9513, NL – 2300 RA Leiden, The Netherlands
Received:
21
September
2004
Accepted:
10
January
2005
We present the results of observations from the Plateau de Bure
IRAM interferometric array of the submillimetre (submm) galaxy SMMJ16359+6612 lying at  behind the
core of the massive cluster A 2218. The foreground gravitational lens
produces three images with a total magnification of 45 of this faint
submm galaxy, which has an intrinsic submm flux of just
behind the
core of the massive cluster A 2218. The foreground gravitational lens
produces three images with a total magnification of 45 of this faint
submm galaxy, which has an intrinsic submm flux of just  mJy – placing it below the confusion limit of blank-field
surveys. The substantial magnification provides a rare opportunity to
probe the nature of a distant sub-mJy submm-selected galaxy, part of
the population which produces the bulk of the cosmic far-infrared
background at submm wavelengths. Our observations detect the CO(3–2) line in all three images, as well as the CO(7–6) line and the dust continuum at 1.3 mm for the brightest image
but only at a 3σ level. The velocity profile of
the CO(3–2) line displays a double-peak profile which is well fit by
two Gaussians with FWHM of 220 km s-1 and separated by 280 km s-1. We
estimate the dynamical mass of the system to be ~1.5
mJy – placing it below the confusion limit of blank-field
surveys. The substantial magnification provides a rare opportunity to
probe the nature of a distant sub-mJy submm-selected galaxy, part of
the population which produces the bulk of the cosmic far-infrared
background at submm wavelengths. Our observations detect the CO(3–2) line in all three images, as well as the CO(7–6) line and the dust continuum at 1.3 mm for the brightest image
but only at a 3σ level. The velocity profile of
the CO(3–2) line displays a double-peak profile which is well fit by
two Gaussians with FWHM of 220 km s-1 and separated by 280 km s-1. We
estimate the dynamical mass of the system to be ~1.5 
 and an H2 gas mass of 4.5
and an H2 gas mass of 4.5 
 . We identify a spatial offset of ~
. We identify a spatial offset of ~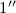 between the two CO(3–2) velocity components, again benefiting from the magnification due
to the foreground lens, modeling of which indicates that the offset
corresponds to just ~3 kpc in projection at
between the two CO(3–2) velocity components, again benefiting from the magnification due
to the foreground lens, modeling of which indicates that the offset
corresponds to just ~3 kpc in projection at  . The spatial
and velocity properties of these two components are closely related to
features detected in previously published Hα spectroscopy. We
propose that this source is a compact merger of
two typical Lyman-break galaxies with a maximal separation between
the two nuclei of about 3 kpc, although a dusty disk explanation is not
excluded. This system is much less luminous and massive than
other high-redshift submillimetre galaxies studied to date, but it
bears a close similarity to similarly luminous, dusty starburst
resulting from lower-mass mergers in the local Universe.
. The spatial
and velocity properties of these two components are closely related to
features detected in previously published Hα spectroscopy. We
propose that this source is a compact merger of
two typical Lyman-break galaxies with a maximal separation between
the two nuclei of about 3 kpc, although a dusty disk explanation is not
excluded. This system is much less luminous and massive than
other high-redshift submillimetre galaxies studied to date, but it
bears a close similarity to similarly luminous, dusty starburst
resulting from lower-mass mergers in the local Universe.
Key words: gravitational lensing / cosmology: observations / galaxies: clusters: individual: A2219 / galaxies: high-redshift / infrared: galaxies / galaxies: individual: SMM J16359+6612
© ESO, 2005
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


