| Issue |
A&A
Volume 433, Number 1, April I 2005
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 385 - 393 | |
| Section | Celestial mechanics and astrometry | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20047155 | |
| Published online | 14 March 2005 | |
On the possibility of measuring the solar oblateness and some relativistic effects from planetary ranging
Dipartimento di Fisica dell'Universita di Bari, via Amendola 173, 70126 Bari, Italy e-mail: lorenzo.iorio@libero.it
Received:
27
January
2004
Accepted:
3
December
2004
In this paper we first calculate the post-Newtonian
gravitoelectric secular rate of the mean anomaly of a test
particle freely orbiting a spherically symmetric central mass.
Then, we propose a novel approach to suitably combine the
presently available planetary ranging data to Mercury, Venus and
Mars in order to determine, simultaneously and independently of
each other, the Sun's quadrupole mass moment  and the
secular advances of the perihelion and the mean anomaly. This
would also allow to obtain the PPN parameters γ and β
independently. We propose to analyze the time series of three
linear combinations of the observational residuals of the rates of
the nodes
and the
secular advances of the perihelion and the mean anomaly. This
would also allow to obtain the PPN parameters γ and β
independently. We propose to analyze the time series of three
linear combinations of the observational residuals of the rates of
the nodes 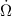 , the longitudes of perihelia
, the longitudes of perihelia 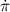 and
mean anomalies
and
mean anomalies  of Mercury, Venus and Mars
suitably built up in order to absorb the secular precessions
induced by the solar oblateness and the post-Newtonian
gravitoelectric forces. The values of the three investigated
parameters can be obtained by fitting the expected linear trends
with straight lines, determining their slopes in arcseconds per
century and suitably normalizing them. According to the
present-day EPM2000 and DE405 ephemerides accuracy, the obtainable
precision would be of the order of 10-3–10-4 for the
PPN parameters and, more interestingly, of 10-9 for
of Mercury, Venus and Mars
suitably built up in order to absorb the secular precessions
induced by the solar oblateness and the post-Newtonian
gravitoelectric forces. The values of the three investigated
parameters can be obtained by fitting the expected linear trends
with straight lines, determining their slopes in arcseconds per
century and suitably normalizing them. According to the
present-day EPM2000 and DE405 ephemerides accuracy, the obtainable
precision would be of the order of 10-3–10-4 for the
PPN parameters and, more interestingly, of 10-9 for  . It must be pointed out that the future BepiColombo mission should improve the knowledge of the Mercury's orbit
perhaps by one order of magnitude.
. It must be pointed out that the future BepiColombo mission should improve the knowledge of the Mercury's orbit
perhaps by one order of magnitude.
Key words: relativity / gravitation / celestial mechanics / Sun: fundamental parameters / planets and satellites: general
© ESO, 2005
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


