| Issue |
A&A
Volume 432, Number 2, March III 2005
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 633 - 645 | |
| Section | Stellar atmospheres | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20041732 | |
| Published online | 02 March 2005 | |
Hydrodynamic model atmospheres for WR stars
Self-consistent modeling of a WC star wind
1
Institut für Physik, Astrophysik, Universität Potsdam, Am Neuen Palais 10, 14469 Potsdam, Germany e-mail: goetz@astro.physik.uni-potsdam.de
2
Institute of Astronomy, ETH Zentrum SEC , Scheuchzer Str. 7, 8092 Zürich, Switzerland
3
PMOD/WRC, 7260 Davos Dorf, Switzerland
Received:
26
July
2004
Accepted:
20
October
2004
We present the first non-LTE atmosphere models for WR stars that
incorporate a self-consistent solution of the hydrodynamic equations. The
models take iron-group line-blanketing and clumping into account, and compute
the hydrodynamic structure of a radiatively driven wind consistently with the
non-LTE radiation transport in the co-moving frame. We construct a
self-consistent wind model that reproduces all observed properties of an
early-type WC star (WC5). We find that the WR-type mass-loss is initiated at
high optical depth by the so-called “Hot Iron Bump” opacities (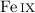 –xvi). The acceleration of the outer wind regions is due to iron-group ions
of lower excitation in combination with C and O. Consequently, the wind
structure shows two acceleration regions, one close to the hydrostatic wind
base in the optically thick part of the atmosphere, and another farther out in
the wind. In addition to the radiative acceleration, the “Iron Bump” opacities
are responsible for an intense heating of deep atmospheric layers. We find
that the observed narrow
–xvi). The acceleration of the outer wind regions is due to iron-group ions
of lower excitation in combination with C and O. Consequently, the wind
structure shows two acceleration regions, one close to the hydrostatic wind
base in the optically thick part of the atmosphere, and another farther out in
the wind. In addition to the radiative acceleration, the “Iron Bump” opacities
are responsible for an intense heating of deep atmospheric layers. We find
that the observed narrow 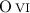 emission lines in the optical spectra of
WC stars originate from this region. From their dependence on the clumping
factor we gain important information about the location where the density
inhomogeneities in WR-winds start to develop.
emission lines in the optical spectra of
WC stars originate from this region. From their dependence on the clumping
factor we gain important information about the location where the density
inhomogeneities in WR-winds start to develop.
Key words: stars: Wolf-Rayet / stars: early-type / stars: atmospheres / stars: mass-loss / stars: winds, outflows / stars: individual: WR 111
© ESO, 2005
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


