| Issue |
A&A
Volume 430, Number 2, February I 2005
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | L41 - L44 | |
| Section | Letters | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:200400129 | |
| Published online | 20 January 2005 | |
Letter to the Editor
The ionization structure of early-B supergiant winds
1
Department of Physics & Astronomy, University College London, Gower Street, London WC1E 6BT, UK e-mail: [rkp;scs]@star.ucl.ac.uk
2
SGT, Inc., Code 681.0, NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD 20771, USA e-mail: massa@taotaomona.gsfc.nasa.gov
Received:
18
October
2004
Accepted:
15
December
2004
We present empirically determined ionization conditions for the winds of
106 luminous B0 to B5 stars observed by IUE. The UV wind lines are
modelled to extract products of mass-loss rates times ionization fractions
(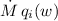 , where
, where  ) for N v, C iv,
Si iv, Si iii, Al iii and C ii. We describe
the general behaviour of the
) for N v, C iv,
Si iv, Si iii, Al iii and C ii. We describe
the general behaviour of the 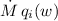 and their ratios,
demonstrating that the wind ionization increases with distance from
the star, contrary to recent findings for O star winds. Using empirical
mass-loss rates (from Hα observations) and model
prescriptions, we derive mean
and their ratios,
demonstrating that the wind ionization increases with distance from
the star, contrary to recent findings for O star winds. Using empirical
mass-loss rates (from Hα observations) and model
prescriptions, we derive mean 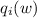 values integrated over the wind,
values integrated over the wind,
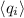 . These
. These 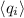 are quite small, never
exceeding 15% for Al iii or 2% for Si iv. This is
surprising, since the
are quite small, never
exceeding 15% for Al iii or 2% for Si iv. This is
surprising, since the 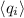 for these ions clearly peak
within the observed spectral range. We conclude that the low
for these ions clearly peak
within the observed spectral range. We conclude that the low
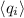 arise because the
arise because the 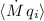 are
underestimated by the wind models, which assume that the outflows are
smooth when they are, in fact, highly structured.
are
underestimated by the wind models, which assume that the outflows are
smooth when they are, in fact, highly structured.
Key words: stars: early-type / stars: mass-loss / ultraviolet: stars
© ESO, 2005
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


