| Issue |
A&A
Volume 427, Number 3, December I 2004
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 803 - 814 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20041410 | |
| Published online | 16 November 2004 | |
A top-down scenario for the formation of massive Tidal Dwarf Galaxies
1
CEA/DSM/DAPNIA, Service d'Astrophysique, Saclay, 91191 Gif-sur-Yvette Cedex, France e-mail: paduc@cea.fr
2
CNRS, FRE 2591
3
Observatoire de Paris, LERMA, 61 Av. de l'Observatoire, 75014 Paris, France
4
École Normale Supérieure, 45 rue d'Ulm, 75005 Paris, France
Accepted: 4 June 2004
Among those objects formed out of collisional debris during galaxy mergers, the prominent
gaseous accumulations observed near the tip of some long tidal tails are the
most likely to survive long enough to form genuine recycled galaxies.
Using simple numerical models, [CITE] claimed that
tidal objects as massive as 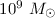 could only form, in these simulations, within
extended dark matter (DM) haloes. We present here a new set of simulations
of galaxy collisions to further investigate the structure of tidal tails. First of all,
we checked that massive objects are still produced in full N-body codes that
include feedback and a large number of particles. Using a simpler N-body code with
rigid haloes, we
noticed that dissipation and self-gravity in the tails, although important, are not the key
factors. Exploiting toy models, we found that, for truncated DM haloes,
material is stretched along the tail, while, within extended haloes, the tidal field
can efficiently carry away from the disk a large fraction of the gas, while maintaining
its surface density to a high value. This creates a density enhancement near the tip
of the tail. Only later-on, self-gravity takes over; the gas clouds collapse and start
forming stars. Thus, such objects were
fundamentally formed following a kinematical process, according to a top-down
scenario, contrary to the less massive Super Star Clusters that are also
present around mergers. This conclusion leads us to introduce a restrictive
definition for Tidal Dwarf Galaxies (TDGs) and their progenitors, considering only
the most massive ones, initially mostly made of gas, that were able to pile up in
the tidal tails. More simulations will be necessary to precisely determine the
fate of these proto–TDGs and estimate their number.
could only form, in these simulations, within
extended dark matter (DM) haloes. We present here a new set of simulations
of galaxy collisions to further investigate the structure of tidal tails. First of all,
we checked that massive objects are still produced in full N-body codes that
include feedback and a large number of particles. Using a simpler N-body code with
rigid haloes, we
noticed that dissipation and self-gravity in the tails, although important, are not the key
factors. Exploiting toy models, we found that, for truncated DM haloes,
material is stretched along the tail, while, within extended haloes, the tidal field
can efficiently carry away from the disk a large fraction of the gas, while maintaining
its surface density to a high value. This creates a density enhancement near the tip
of the tail. Only later-on, self-gravity takes over; the gas clouds collapse and start
forming stars. Thus, such objects were
fundamentally formed following a kinematical process, according to a top-down
scenario, contrary to the less massive Super Star Clusters that are also
present around mergers. This conclusion leads us to introduce a restrictive
definition for Tidal Dwarf Galaxies (TDGs) and their progenitors, considering only
the most massive ones, initially mostly made of gas, that were able to pile up in
the tidal tails. More simulations will be necessary to precisely determine the
fate of these proto–TDGs and estimate their number.
Key words: galaxies: formation / galaxies: interactions / galaxies: dwarf / galaxies: halos / cosmology: dark matter
© ESO, 2004
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


