| Issue |
A&A
Volume 426, Number 2, November I 2004
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 567 - 575 | |
| Section | Interstellar and circumstellar matter | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20041176 | |
| Published online | 11 October 2004 | |
The supernova remnant G 6.4-0.1 and its environment
1
University of Crete, Physics Department, PO Box 2208, 71003 Heraklion, Crete, Greece e-mail: fotis@physics.uoc.gr
2
Institute of Astronomy & Astrophysics, National Observatory of Athens, I. Metaxa & V. Pavlou, P. Penteli, 15236 Athens, Greece
Received:
28
April
2004
Accepted:
12
July
2004
Flux calibrated CCD images, in the H
 ], [
], [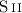 ], and [
], and [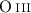 ]
emission lines, of a wide field around the supernova remnant
G 6.4-0.1 are presented.
The low ionization images identify a front of enhanced
[
]
emission lines, of a wide field around the supernova remnant
G 6.4-0.1 are presented.
The low ionization images identify a front of enhanced
[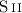 ]/H
]/H
 ] ratio along the east-west direction.
This front is very well correlated with the filamentary radio
emission of the remnant as well as with molecular CO emission
and may indicate the interaction of the primary blast wave with
molecular clouds present in the vicinity of the remnant.
We estimate a total Hα flux, corrected for interstellar extinction,
of 2
] ratio along the east-west direction.
This front is very well correlated with the filamentary radio
emission of the remnant as well as with molecular CO emission
and may indicate the interaction of the primary blast wave with
molecular clouds present in the vicinity of the remnant.
We estimate a total Hα flux, corrected for interstellar extinction,
of 2  10-8 erg s-1 cm-2, and a total [
10-8 erg s-1 cm-2, and a total [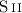 ] flux
of 1.1
] flux
of 1.1  10-8 erg s-1 cm-2.
The H
10-8 erg s-1 cm-2.
The H
 ] and [
] and [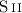 ] images provide evidence for the
presence of emission from shock heated gas to the south-west and
to the east of the bulk of the known optical emission, implying
that the primary shock wave is able to drive radiative shocks
into the interstellar clouds.
The image in the medium ionization line of [
] images provide evidence for the
presence of emission from shock heated gas to the south-west and
to the east of the bulk of the known optical emission, implying
that the primary shock wave is able to drive radiative shocks
into the interstellar clouds.
The image in the medium ionization line of [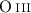 ]5007 Å does not reveal
any filamentary structures. On the contrary, the emission is diffuse and
very weak, close to our detection limit of 5
]5007 Å does not reveal
any filamentary structures. On the contrary, the emission is diffuse and
very weak, close to our detection limit of 5  10-17 erg s-1 cm-2 arcsec-2 (3σ), and appears to be mainly
present in the south-east to north-west areas of the remnant.
The long-slit spectra
indicate significant extinction in all positions observed, while
the measured variations are within the 3σ error. The [
10-17 erg s-1 cm-2 arcsec-2 (3σ), and appears to be mainly
present in the south-east to north-west areas of the remnant.
The long-slit spectra
indicate significant extinction in all positions observed, while
the measured variations are within the 3σ error. The [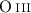 ]
emission in the spectra, whenever present, is weaker than the Hβ flux
suggesting shock velocities around 70 km s-1 or less all around the
remnant in accordance with the [
]
emission in the spectra, whenever present, is weaker than the Hβ flux
suggesting shock velocities around 70 km s-1 or less all around the
remnant in accordance with the [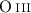 ] imagery. Thus, the low shock
velocities are a common characteristic of G 6.4-0.1 and not just of the areas
where the spectra were acquired. The average sulfur line ratio suggests
postshock electron densities below 120 cm-3 at the 3σ limit.
] imagery. Thus, the low shock
velocities are a common characteristic of G 6.4-0.1 and not just of the areas
where the spectra were acquired. The average sulfur line ratio suggests
postshock electron densities below 120 cm-3 at the 3σ limit.
Key words: ISM: general / ISM: supernova remnants / ISM: individual objects: G 6.4-0.1
© ESO, 2004
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


