| Issue |
A&A
Volume 426, Number 2, November I 2004
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 707 - 715 | |
| Section | Atomic, molecular, and nuclear data | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20047188 | |
| Published online | 11 October 2004 | |
Collisional depolarization and transfer rates of spectral lines by atomic hydrogen
IV. Application to ionised atoms
1
Observatoire de Paris-Meudon, LERMA UMR CNRS 8112, 5, Place Jules Janssen, 92195 Meudon Cedex, France
2
Observatoire de Paris-Meudon, LERMA UMR CNRS 8112, 5, Place Jules Janssen, 92195 Meudon Cedex, France Department of Astronomy and Space Physics, Uppsala University, Box 515, 75120 Uppsala, Sweden e-mail: Moncef.Derouich@obspm.fr
Received:
9
February
2004
Accepted:
29
June
2004
The semi-classical
theory of collisional depolarization of spectral lines
that we have applied to neutral atoms in previous papers
is extended to spectral lines
of singly ionised atoms. In order
to validate our general theory, we compare our results to
quantum chemistry calculations obtained for the particular cases of the 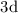
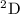 and
and
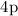
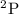 states of the CaII ion. As a demonstration of the universality
of our theory and the easiness of its application, we calculate
depolarization and polarization
transfer rates for the
states of the CaII ion. As a demonstration of the universality
of our theory and the easiness of its application, we calculate
depolarization and polarization
transfer rates for the 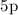
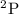 state of the SrII
ion. Analytical
expressions of all rates as a function of local temperature are given.
Our results for the CaII ion are compared to recent quantum chemistry
calculations. A discussion of our results is presented.
state of the SrII
ion. Analytical
expressions of all rates as a function of local temperature are given.
Our results for the CaII ion are compared to recent quantum chemistry
calculations. A discussion of our results is presented.
Key words: Sun: atmosphere / atomic processes / line: formation / polarization
© ESO, 2004
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


