| Issue |
A&A
Volume 423, Number 1, August III 2004
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 13 - 19 | |
| Section | Astrophysical processes | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20047065 | |
| Published online | 29 July 2004 | |
Radio emission and particle acceleration in plerionic supernova remnants
Institute for Astronomy and Astrophysics, University of Munich, Germany e-mail: nodes@usm.uni-muenchen.de
Received:
13
January
2004
Accepted:
7
May
2004
Plerionic supernova remnants exhibit radio emission with remarkably
flat spectral indices ranging from 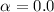 to
to  . The origin
of very hard particle energy distributions still awaits an explanation,
since shock waves generate particle distributions with synchrotron spectra
characterized by
. The origin
of very hard particle energy distributions still awaits an explanation,
since shock waves generate particle distributions with synchrotron spectra
characterized by 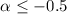 . Acceleration of high energy leptons in
magnetohydrodynamic turbulence instead may be responsible for the observed
hard spectra. This process is studied by means of relativistic test particle
calculations using electromagnetic fields produced by three-dimensional
simulations of resistive magnetohydrodynamical turbulence. The particles
receive power-law energy spectra
. Acceleration of high energy leptons in
magnetohydrodynamic turbulence instead may be responsible for the observed
hard spectra. This process is studied by means of relativistic test particle
calculations using electromagnetic fields produced by three-dimensional
simulations of resistive magnetohydrodynamical turbulence. The particles
receive power-law energy spectra  with s
ranging from 1.2 to 1.6, i.e. particle spectra that are required to
explain the radio emission of plerions.
with s
ranging from 1.2 to 1.6, i.e. particle spectra that are required to
explain the radio emission of plerions.
Key words: stars: pulsars: individual: Crab / radio continuum: stars / acceleration of particles / turbulence
© ESO, 2004
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


