| Issue |
A&A
Volume 422, Number 3, August II 2004
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 925 - 940 | |
| Section | Extragalactic astronomy | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20035652 | |
| Published online | 16 July 2004 | |
Profile variability of the H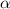 and H
and H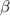 broad
emission lines in NGC 5548 *,**
broad
emission lines in NGC 5548 *,**
1
Special Astrophysical Observatory of the Russian AS, Nizhnij Arkhyz, Karachaevo-Cherkesia 369167, Russia e-mail: ashap@sao.ru
2
Isaac Newton Institute of Chile, SAO Branch, Russia
3
Sternberg Astronomical Institute, University of Moscow, Universitetskij Prospect 13, Moscow 119899, Russia
4
Isaac Newton Institute of Chile, Crimean Branch, Ukraine
5
Instituto Nacional de Astrofísica, Optica y Electrónica, INAOE, Apartado Postal 51 y 216, 7200 Puebla, Pue., Mexico
6
LUTH, Observatoire de Paris, Section de Meudon, place Janssen, 92195 Meudon, France
7
Benemérita Universidad Autónoma de Puebla, Facultad de Ciencias Físico-Matemáticas, Apdo. Postal 1152, CP 72000 Puebla, Pue., Mexico
Received:
10
November
2003
Accepted:
26
April
2004
Between 1996 and 2002, we have carried out a spectral
monitoring program for the Seyfert galaxy NGC 5548 with
the 6 m and 1 m telescopes of SAO (Russia) and with the 2.1 m
telescope of Guillermo Haro Observatory (GHO) at Cananea,
Mexico. High quality spectra with 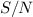 > 50 in the continuum
near Hα and Hβ were obtained, covering the spectral
range ~(4000–7500) Å with a (4.5 to 15) Å-resolution. We found that both the flux in the lines and the
continuum gradually decreased, reaching minimum values during
May–June 2002. In the minimum state, the wings of Hβ and
Hα became extremely weak, corresponding to a Sy1.8 type,
not to a Sy1, as observed previously when the nucleus was
brighter. The line profiles were decomposed into variable and
constant components. The variable broad component is well
correlated with the continuum variation. It consists of a double
peaked structure with radial velocities ~±1000 km s-1
relative to the narrow component. A constant component, whose
presence is independent of the continuum flux variations, shows
only narrow emission lines.The mean, rms, and the averaged over
years, observed and difference line profiles of Hβ and
Hα reveal the same double peaked structure. The relative
intensity of these peaks changes with time. During 1996, the red
peak was the brightest, while in 1998–2002, the blue peak
became the brighter one. Their radial velocities vary in the
~(500–1200) km s-1 range. In 2000–2002 a distinct third
peak appeared in the red wing of Hα and Hβ line
profiles. The radial velocity of this feature decreased between
2000 and 2002: from the observed profiles, from ~+(2500–2600) km s-1 to ~+2000 km s-1 and is clearly seen on the
difference profiles. The fluxes of the various parts of the line
profiles are well correlated with each other and also with the
continuum flux. The blue and red parts of the line profiles at
the same radial velocities vary in an almost identical manner.
Shape changes of the different parts of the broad line are not
correlated with continuum variations and, apparently, are not
related to reverberation effects. Changes of the integral Balmer
decrement are, on average, anticorrelated with the continuum flux
variations. This is probably due to an increasing role of
collisional excitation as the ionizing flux decreases.
The behavior of the
Balmer decrement of the various parts of the line profiles was
different in 1996–2000 as compared with the 2001 behavior. Our
results favor the formation of the broad Balmer lines
in a turbulent
accretion disc with large and moving
“optically thick” inhomogeneities, capable of reprocessing the central source continuum.
> 50 in the continuum
near Hα and Hβ were obtained, covering the spectral
range ~(4000–7500) Å with a (4.5 to 15) Å-resolution. We found that both the flux in the lines and the
continuum gradually decreased, reaching minimum values during
May–June 2002. In the minimum state, the wings of Hβ and
Hα became extremely weak, corresponding to a Sy1.8 type,
not to a Sy1, as observed previously when the nucleus was
brighter. The line profiles were decomposed into variable and
constant components. The variable broad component is well
correlated with the continuum variation. It consists of a double
peaked structure with radial velocities ~±1000 km s-1
relative to the narrow component. A constant component, whose
presence is independent of the continuum flux variations, shows
only narrow emission lines.The mean, rms, and the averaged over
years, observed and difference line profiles of Hβ and
Hα reveal the same double peaked structure. The relative
intensity of these peaks changes with time. During 1996, the red
peak was the brightest, while in 1998–2002, the blue peak
became the brighter one. Their radial velocities vary in the
~(500–1200) km s-1 range. In 2000–2002 a distinct third
peak appeared in the red wing of Hα and Hβ line
profiles. The radial velocity of this feature decreased between
2000 and 2002: from the observed profiles, from ~+(2500–2600) km s-1 to ~+2000 km s-1 and is clearly seen on the
difference profiles. The fluxes of the various parts of the line
profiles are well correlated with each other and also with the
continuum flux. The blue and red parts of the line profiles at
the same radial velocities vary in an almost identical manner.
Shape changes of the different parts of the broad line are not
correlated with continuum variations and, apparently, are not
related to reverberation effects. Changes of the integral Balmer
decrement are, on average, anticorrelated with the continuum flux
variations. This is probably due to an increasing role of
collisional excitation as the ionizing flux decreases.
The behavior of the
Balmer decrement of the various parts of the line profiles was
different in 1996–2000 as compared with the 2001 behavior. Our
results favor the formation of the broad Balmer lines
in a turbulent
accretion disc with large and moving
“optically thick” inhomogeneities, capable of reprocessing the central source continuum.
Key words: galaxies: active / galaxies: Seyfert / galaxies: individual: NGC 5548 / line: profiles
© ESO, 2004
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


