| Issue |
A&A
Volume 422, Number 2, August I 2004
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 603 - 608 | |
| Section | Interstellar and circumstellar matter | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20047096 | |
| Published online | 09 July 2004 | |
Candidates for giant lobes projecting from the LBV stars P Cygni and R 143
1
Jodrell Bank Observatory, University of Manchester, Macclesfield SK11 9DL, UK
2
Institute of Astronomy & Astrophysics, National Observatory of Athens, I. Metaxa & V. Paulou, P. Penteli, GR-15236 Athens, Greece
3
Dublin Institute for Advanced Studies, School of Cosmic Physics, 5 Merrion Square, Dublin 2, Republic of Ireland
4
Instituto de Astronomia, UNAM, Apdo. Postal 877. Ensenada, BC 22800, México
5
University of Crete, Physics Department, PO Box 2208, 710 03 Heraklion, Crete, Greece
Corresponding author: J. Meaburn, jm@ast.man.ac.uk
Received:
19
January
2004
Accepted:
6
April
2004
Deep, wide-field, continuum-subtracted, images in the light of the
Hα + [N ii] 6548 & 6584 Å and [O iii]5007 Å nebular emission lines have been obtained of the
environment of the Luminous Blue Variable (LBV) star P Cygni.
A previously discovered, receding, nebulous filament along PA 50°
has now been
shown to extend up to 12´ from this star. Furthermore, in the
light of [O iii]5007 Å, a southern counterpart is discovered as well as
irregular filaments on the opposite side of P Cygni.
Line profiles from this nebulous complex indicate that this
extended nebulosity is similar to that associated with
middle-aged supernova remnants. However, there are several indications
that it has originated in P Cygni and is not just a chance superposition
along the same sight-line. This possibility is explored here and comparison
is made with a new image of the LBV star R 143 in the LMC from which similar
filaments appear to project.
The dynamical age of the P Cygni giant lobe of ≈5  104 yr
is consistent with both the predicted and observed durations of
the LBV phases of 50
104 yr
is consistent with both the predicted and observed durations of
the LBV phases of 50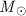 stars after they have left the main sequence.
Its irregular shape may have been determined by the cavity
formed in the ambient gas by the energetic wind of the star, and
shaped by a dense torus,
when on the main sequence.
The proper motion and radial velocity of P Cygni,
with respect to its local environment,
could explain the observed angular and kinematical shifts of the star
compared with the giant lobe.
stars after they have left the main sequence.
Its irregular shape may have been determined by the cavity
formed in the ambient gas by the energetic wind of the star, and
shaped by a dense torus,
when on the main sequence.
The proper motion and radial velocity of P Cygni,
with respect to its local environment,
could explain the observed angular and kinematical shifts of the star
compared with the giant lobe.
Key words: stars: circumstellar matter
© ESO, 2004
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


