| Issue |
A&A
Volume 412, Number 3, December IV 2003
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 897 - 902 | |
| Section | Astronomical instrumentation | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20031432 | |
| Published online | 08 December 2003 | |
The nature of the fiber noise with the FOCES spectrograph
Nature, modeling and a way to achieve
S/N 
Universitäts Sternwarte München, Scheinerstr. 1, 12345 München, Germany
Corresponding author: fug@usm.uni-muenchen.de
Received:
15
April
2003
Accepted:
8
September
2003
The non-white noise noticed using the fiber-fed Foces
spectrograph is recognized as the result of vignetting to an
uneven distribution of monochromatic light in the
spectrograph beam behind the fiber exit. This phenomenon –
that can be assigned to every fiber-coupled spectrograph
with vignetting of the light path behind the fiber –
is qualitatively and quantitatively described and modeled.
The 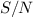 ratio
that seemed to be limited to ≈200 when surrounding
the object exposure by two flatfield exposures is shown to
reach the theoretical limit (defined by the linear range of
the CCD-detector) of
ratio
that seemed to be limited to ≈200 when surrounding
the object exposure by two flatfield exposures is shown to
reach the theoretical limit (defined by the linear range of
the CCD-detector) of 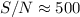 . This is achieved by
using multiple flatfield exposures in combination with a
fiber vibration device allowing non-harmonic movement
of the fiber during exposure time.
. This is achieved by
using multiple flatfield exposures in combination with a
fiber vibration device allowing non-harmonic movement
of the fiber during exposure time.
Key words: instrumentation: spectrographs / techniques: spectroscopic / telescopes
© ESO, 2003
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


