| Issue |
A&A
Volume 410, Number 2, November I 2003
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 397 - 414 | |
| Section | Astrophysical processes | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20031103 | |
| Published online | 17 November 2003 | |
Nonthermal radiation from jets of active galactic nuclei: Electrostatic bremsstrahlung as alternative to synchrotron radiation
Institut für Theoretische Physik, Lehrstuhl IV: Weltraum- und Astrophysik, Ruhr-Universität Bochum, 44780 Bochum, Germany
Corresponding author: rsch@tp4.ruhr-uni-bochum.de
Received:
1
April
2003
Accepted:
4
July
2003
The interaction of collimated relativistic hadronic
and leptonic jet outflows from active galactic nuclei
with the surrounding interstellar and intergalactic medium generates by two-stream instabilities huge
intensities of subluminal electrostatic (Langmuir) wave fields in the co-moving outflow region
with energy densities larger than the energy density in the magnetic field. We therefore revisit
electrostatic bremsstrahlung, i.e. the inverse Compton scattering of electrostatic waves by energetic
positrons and electrons to photons (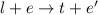 ), as an alternative nonthermal radiation process
to synchrotron radiation which in the literature sofar has been the standard low-frequency
radiation process for radiation. It is known that this radiation process has similar polarisation properties
as synchrotron radiation.
By calculating Doppler boosted luminosity spectra in case of leptonic outflows
we demonstrate that in jet outflow sources electrostatic bremsstrahlung by swept-up relativistic
electrons is stronger than synchrotron radiation from the same electrons in the
radio to optical frequency band, whereas the optically thick bulk electrostatic bremsstrahlung
from the non-relativistic pair outflow plasma is typically a factor 1010 smaller.
Our analysis is based on photon angle integrated monochromatic approximations of the
electrostatic bremsstrahlung power and synchrotron radiation power in a plasma, which are constructed
from moments of the respective radiation powers of single electrons and positrons.
Specialising to the specific subluminal electrostatic wave distribution and
the swept-up relaivistic electrons in the leptonic jet model of Schlickeiser et al. ([CITE])
we calculate the expected Doppler boosted radiation intensities from bulk electrostatic bremsstrahlung,
relativistic electron bremsstrahlung and synchrotron radiation for standard inner jet parameters.
This requires to investigate
in detail (i) the equilibrium distribution of the radiating electrons and (ii) the
emission and absorption coefficients of each radiation process.
An attractive feature of electrostatic bremsstrahlung mechanism is the fact that the
interaction of the jet outflow
with the surrounding ambient medium generates both the target electrostatic plasma waves and the radiating
swept-up relativistic electrons. It does not rely on the existence of large intrinsic ordered
magnetic fields to account for strong emission due to the synchrotron radiation process.
This might be of importance also for nonthermal emission far away from the central jet engine.
), as an alternative nonthermal radiation process
to synchrotron radiation which in the literature sofar has been the standard low-frequency
radiation process for radiation. It is known that this radiation process has similar polarisation properties
as synchrotron radiation.
By calculating Doppler boosted luminosity spectra in case of leptonic outflows
we demonstrate that in jet outflow sources electrostatic bremsstrahlung by swept-up relativistic
electrons is stronger than synchrotron radiation from the same electrons in the
radio to optical frequency band, whereas the optically thick bulk electrostatic bremsstrahlung
from the non-relativistic pair outflow plasma is typically a factor 1010 smaller.
Our analysis is based on photon angle integrated monochromatic approximations of the
electrostatic bremsstrahlung power and synchrotron radiation power in a plasma, which are constructed
from moments of the respective radiation powers of single electrons and positrons.
Specialising to the specific subluminal electrostatic wave distribution and
the swept-up relaivistic electrons in the leptonic jet model of Schlickeiser et al. ([CITE])
we calculate the expected Doppler boosted radiation intensities from bulk electrostatic bremsstrahlung,
relativistic electron bremsstrahlung and synchrotron radiation for standard inner jet parameters.
This requires to investigate
in detail (i) the equilibrium distribution of the radiating electrons and (ii) the
emission and absorption coefficients of each radiation process.
An attractive feature of electrostatic bremsstrahlung mechanism is the fact that the
interaction of the jet outflow
with the surrounding ambient medium generates both the target electrostatic plasma waves and the radiating
swept-up relativistic electrons. It does not rely on the existence of large intrinsic ordered
magnetic fields to account for strong emission due to the synchrotron radiation process.
This might be of importance also for nonthermal emission far away from the central jet engine.
Key words: galaxies: active / galaxies: jets / radiation mechanisms: non-thermal / plasmas
© ESO, 2003
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


