| Issue |
A&A
Volume 408, Number 2, September III 2003
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 581 - 599 | |
| Section | Interstellar and circumstellar matter | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20030942 | |
| Published online | 17 November 2003 | |
Determination of the gas-to-dust ratio in nearby dense clouds using X-ray absorption measurements
1
Service d'Astrophysique, CEA Saclay, 91191 Gif-sur-Yvette, France
2
Laboratoire d'Astrophysique de Grenoble, Université Joseph Fourier, BP 53, 38041 Grenoble Cedex 9, France
3
Department of Astronomy & Astrophysics, 525 Davey Laboratory, Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA 16802, USA
4
Institut d'Astrophysique Spatiale, Bât. 121, Université de Paris XI, 91405 Orsay Cedex, France
Corresponding author: M. H. Vuong, vuong@discovery.saclay.cea.fr
Received:
17
March
2003
Accepted:
18
June
2003
We present a comparison of the gas and dust properties of the dense interstellar matter in six nearby star-forming regions (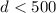 pc): ρ Oph, Cha I, R CrA, IC 348, NGC 1333, and Orion. We measure from Chandra and XMM-Newton observations the X-ray absorption toward pre-main sequence stars (PMS) without accretion disks (i.e., Class III sources) to obtain the total hydrogen column density NH,X. For these sources we take from the literature the corresponding dust extinction in the near-infrared, AJ, or when unavailable we derive it from SED fitting using the available DENIS, 2MASS, ISOCAM and other data. We then compare NH,X and AJ for each object, up to unprecedently high extinction. For the ρ Oph dark cloud with a relatively large sample of 20 bona-fide Class III sources, we probe the extinction up to
pc): ρ Oph, Cha I, R CrA, IC 348, NGC 1333, and Orion. We measure from Chandra and XMM-Newton observations the X-ray absorption toward pre-main sequence stars (PMS) without accretion disks (i.e., Class III sources) to obtain the total hydrogen column density NH,X. For these sources we take from the literature the corresponding dust extinction in the near-infrared, AJ, or when unavailable we derive it from SED fitting using the available DENIS, 2MASS, ISOCAM and other data. We then compare NH,X and AJ for each object, up to unprecedently high extinction. For the ρ Oph dark cloud with a relatively large sample of 20 bona-fide Class III sources, we probe the extinction up to 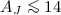 (
(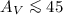 ), and find a best-fit linear relation
), and find a best-fit linear relation 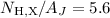 (± 0.4)
(± 0.4)  1021 cm-2 mag-1, adopting standard ISM abundances. The other regions reveal a large dispersion in the NH,X/AJ ratio for each source but for lack of adequate IR data these studies remain limited to moderate extinctions (
1021 cm-2 mag-1, adopting standard ISM abundances. The other regions reveal a large dispersion in the NH,X/AJ ratio for each source but for lack of adequate IR data these studies remain limited to moderate extinctions (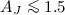 or
or 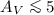 ). For ρ Oph, the
). For ρ Oph, the 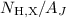 ratio is significantly lower (
ratio is significantly lower (
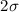 ) than the galactic value, derived using the standard extinction curve (
) than the galactic value, derived using the standard extinction curve (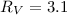 ).
This result is consistent with the recent downwards revision of the metallicity of the Sun and stars in the solar vicinity. We find that the ρ Oph dense cloud has the same metallicity than the local ISM when assuming that the galactic gas-to-dust ratio remains unchanged. The difference between galactic and local values of the gas-to-dust ratio can thus be attributed entirely to a difference in metallicity.
).
This result is consistent with the recent downwards revision of the metallicity of the Sun and stars in the solar vicinity. We find that the ρ Oph dense cloud has the same metallicity than the local ISM when assuming that the galactic gas-to-dust ratio remains unchanged. The difference between galactic and local values of the gas-to-dust ratio can thus be attributed entirely to a difference in metallicity.
Key words: X-rays: stars / stars: pre-main sequence / ISM: clouds / ISM: dust, extinction / open clusters and associations: general
© ESO, 2003
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


