| Issue |
A&A
Volume 405, Number 3, July III 2003
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | L23 - L27 | |
| Section | Letters | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20030731 | |
| Published online | 30 June 2003 | |
Letter to the Editor
Variable polarization in the optical afterglow of GRB 021004*
1
Astronomical Institute, University of Amsterdam, Kruislaan 403, 1098 SJ Amsterdam, The Netherlands
2
Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Aarhus, Ny Munkegade, 8000 Århus, Denmark
3
Astronomical Observatory, University of Copenhagen, Juliane Maries Vej 30, 2100 Copenhagen, Denmark
4
Instituto de Astrofísica de Andalucía, c/ Camino Bajo de Huétor 24, 18.008 Granada, Spain
5
Space Telescope Science Institute, 3700 San Martin Drive, Baltimore, MD 21218, USA
6
Nordic Optical Telescope, Apartado de Correos, 474, 38700 Santa Cruz de La Palma (Tenerife), Spain
7
Real Instituto y Observatorio de la Armada, Sección de Astronomía, 11.110 San Fernando-Naval (Cádiz), Spain
8
Istituto di Astrofisica Spaziale e Fisica Cosmica, Sezione di Bologna, CNR, Via Gobetti 101, 40129 Bologna, Italy
9
INAF, Astronomical Observatory of Trieste, via GB Tiepolo 11, 34131 Trieste, Italy
10
Department of Physical Sciences, University of Hertfordshire, College Lane, Hatfield, Herts AL10 9AB, UK
11
European Southern Obseratory, Alonso de Cordova 3107, Vitacura, Casilla 19001, Santiago 19, Chile
12
NASA MSFC, SD-50 Huntsville, AL 35812, USA
13
European Southern Observatory, Karl-Schwarzschild-Straße 2, 85748 Garching bei München, Germany
Corresponding author: E. Rol, evert@science.uva.nl
Received:
18
March
2003
Accepted:
15
May
2003
We present polarimetric observations of the afterglow of gamma-ray burst (GRB) 021004, obtained with the Nordic Optical Telescope (NOT) and the Very Large Telescope (VLT) between 8 and 17 hours after the burst. Comparison among the observations shows a 45 degree change in the position angle from 9 hours after the burst to 16 hours after the burst, and comparison with published data from later epochs even shows a 90 degree change between 9 and 89 hours after the burst. The degree of linear polarization shows a marginal change, but is also consistent with being constant in time. In the context of currently available models for changes in the polarization of GRBs, a homogeneous jet with an early break time of 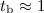 day provides a good explanation of our data. The break time is a factor 2 to 6 earlier than has been found from the analysis of the optical light curve. The change in the position angle of the polarization rules out a structured jet model for the GRB.
day provides a good explanation of our data. The break time is a factor 2 to 6 earlier than has been found from the analysis of the optical light curve. The change in the position angle of the polarization rules out a structured jet model for the GRB.
Key words: gamma rays: bursts / polarization / radiation mechanisms: non-thermal
© ESO, 2003
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


