| Issue |
A&A
Volume 401, Number 2, April II 2003
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 711 - 720 | |
| Section | The Sun | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20030113 | |
| Published online | 21 March 2003 | |
Test particle simulation of the Electron Firehose instability
1
Institute of Astronomy, ETH-Zentrum, 8092 Zurich, Switzerland
2
Paul Scherrer Institute, Würenlingen und Villigen, 5232 Villigen PSI, Switzerland
Corresponding author: G. Paesold, gpaesold@astro.phys.ethz.ch
Received:
10
October
2002
Accepted:
22
January
2003
In the course of the energization of electrons
to energies of some tens of keV during the impulsive phase
of a solar flare, the velocity distribution function of the
electrons is predicted to become anisotropic with 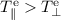 (Here,
(Here, 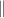 and
and 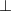 denote directions with respect to the
background magnetic field). Such a configuration can become unstable
to the so-called Electron Firehose instability (EFI).
Left hand circularly polarized electromagnetic waves propagating
along the magnetic field are excited via a non-resonant mechanism:
electrons non-resonantly excite the waves while the protons are in
resonance and carry the wave. The non-resonant nature of the
instability raises the question of the response of the
electron population to the growing waves.
Test particle simulations are carried out to investigate the
pitch-angle development of electrons injected to single waves and
wave spectra. To interpret the simulation results, a drift
kinetic approach is developed. The findings in the case of single wave
simulations show the scattering to larger pitch-angles in excellent
agreement with the theory. The
situation dramatically changes when assuming a spectrum of
waves. Stochasticity is detected at small initial parallel
velocities resulting in significant deviations from drift kinetic
theory. It enhances the scattering rate of electrons with initial
parallel velocity below to the mean thermal perpendicular velocity.
Increased scattering is also noticed for electrons having initial
parallel velocity within an order of magnitude of the resonance
velocity. The resulting pitch-angle scattering is proposed to be an
important ingredient in Fermi-type electron acceleration models,
particularly transit-time acceleration by compressional MHD waves.
denote directions with respect to the
background magnetic field). Such a configuration can become unstable
to the so-called Electron Firehose instability (EFI).
Left hand circularly polarized electromagnetic waves propagating
along the magnetic field are excited via a non-resonant mechanism:
electrons non-resonantly excite the waves while the protons are in
resonance and carry the wave. The non-resonant nature of the
instability raises the question of the response of the
electron population to the growing waves.
Test particle simulations are carried out to investigate the
pitch-angle development of electrons injected to single waves and
wave spectra. To interpret the simulation results, a drift
kinetic approach is developed. The findings in the case of single wave
simulations show the scattering to larger pitch-angles in excellent
agreement with the theory. The
situation dramatically changes when assuming a spectrum of
waves. Stochasticity is detected at small initial parallel
velocities resulting in significant deviations from drift kinetic
theory. It enhances the scattering rate of electrons with initial
parallel velocity below to the mean thermal perpendicular velocity.
Increased scattering is also noticed for electrons having initial
parallel velocity within an order of magnitude of the resonance
velocity. The resulting pitch-angle scattering is proposed to be an
important ingredient in Fermi-type electron acceleration models,
particularly transit-time acceleration by compressional MHD waves.
Key words: acceleration of particules / Sun: flares
© ESO, 2003
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


