| Issue |
A&A
Volume 401, Number 1, April I 2003
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 313 - 323 | |
| Section | Stellar structure and evolution | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20030120 | |
| Published online | 17 March 2003 | |
The mass of the neutron star in Vela X-1 and tidally induced non-radial oscillations in GP Vel
1
Department of Physics and Astronomy, The Open University, Walton Hall, Milton Keynes MK7 6AA, UK
2
Kildrummy Technologies Ltd, 1 Mill Lane, Lerwick, Shetland, ZE1 0AZ, UK
3
Earth and Space Sciences, School of Applied Sciences, University of Glamorgan, Pontypridd CF37 1DL, UK
4
Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Wales, Cardiff CF24 3YB, UK
5
School of Physics, University of Sydney, New South Wales 2006, Australia
6
Department of Physics and Astronomy, The Johns Hopkins University, 3400 North Charles Street, Baltimore, MD 21218-2686, USA
7
Sterrenkundig Instituut “Anton Pannekoek”, Kruislaan 403, 1098 SJ Amsterdam, The Netherlands
Corresponding author: A. J. Norton, a.j.norton@open.ac.uk
Received:
30
September
2002
Accepted:
20
January
2003
We report new radial velocity observations of GP Vel / HD 77581, the
optical companion to the eclipsing X-ray pulsar Vela X-1. Using data spanning
more than two complete orbits of the system, we detect evidence for tidally
induced non-radial oscillations on the surface of GP Vel, apparent as peaks in
the power spectrum of the residuals to the radial velocity curve fit. By
removing the effect of these oscillations (to first order) and binning the
radial velocities, we have determined the semi-amplitude of the radial velocity
curve of GP Vel to be 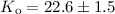 km s-1. Given the
accurately measured semi-amplitude of the pulsar's orbit, the mass ratio of the
system is
km s-1. Given the
accurately measured semi-amplitude of the pulsar's orbit, the mass ratio of the
system is 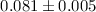 . We are able to set upper and lower limits on the
masses of the component stars as follows. Assuming GP Vel fills its Roche lobe
then the inclination angle of the system, i, is
. We are able to set upper and lower limits on the
masses of the component stars as follows. Assuming GP Vel fills its Roche lobe
then the inclination angle of the system, i, is 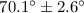 . In this case we obtain the masses of the two stars as
. In this case we obtain the masses of the two stars as  for the neutron star and
for the neutron star and  for GP Vel. Conversely, assuming the inclination angle is
for GP Vel. Conversely, assuming the inclination angle is
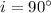 , the ratio of the radius of GP Vel to the radius of its Roche
lobe is
, the ratio of the radius of GP Vel to the radius of its Roche
lobe is 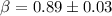 and the masses of the two stars are
and the masses of the two stars are 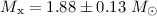 and
and 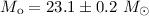 . A
range of solutions between these two sets of limits is also possible,
corresponding to other combinations of i and β. In addition, we note
that if the zero phase of the radial velocity curve is allowed as a free
parameter, rather than constrained by the X-ray ephemeris, a significantly
improved fit is obtained with an amplitude of
. A
range of solutions between these two sets of limits is also possible,
corresponding to other combinations of i and β. In addition, we note
that if the zero phase of the radial velocity curve is allowed as a free
parameter, rather than constrained by the X-ray ephemeris, a significantly
improved fit is obtained with an amplitude of 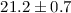 km s-1 and a
phase shift of
km s-1 and a
phase shift of 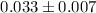 in true anomaly. The apparent shift in the
zero phase of the radial velocity curve may indicate the presence of an
additional radial velocity component at the orbital period. This may be
another manifestation of the tidally induced non-radial oscillations and
provides an additional source of uncertainty in the determination of the
orbital radial velocity amplitude.
in true anomaly. The apparent shift in the
zero phase of the radial velocity curve may indicate the presence of an
additional radial velocity component at the orbital period. This may be
another manifestation of the tidally induced non-radial oscillations and
provides an additional source of uncertainty in the determination of the
orbital radial velocity amplitude.
Key words: binaries: close / stars: neutron / stars: individual: Vela X-1 / stars: individual: GP Vel / stars: individual: HD 77581 / stars: fundamental parameters
© ESO, 2003
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


