| Issue |
A&A
Volume 400, Number 3, March IV 2003
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 971 - 980 | |
| Section | Interstellar and circumstellar matter | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20030033 | |
| Published online | 07 March 2003 | |
Gamma-ray emission from Cassiopeia A produced by accelerated cosmic rays
1
Institute of Cosmophysical Research and Aeronomy, 31 Lenin Ave., 677891 Yakutsk, Russia e-mail: berezhko@ikfia.ysn.ru
2
Max Planck Institut für Kernphysik, Postfach 103980, 69029 Heidelberg, Germany e-mail: Gerd.Puehlhofer@mpi-hd.mpg.de
Corresponding author: H. J. Völk, Heinrich.Voelk@mpi-hd.mpg.de
Received:
23
September
2002
Accepted:
7
January
2003
The nonlinear kinetic model of cosmic ray (CR) acceleration in supernova
remnants (SNRs) is used to describe the relevant properties of
Cassiopeia A (Cas A). In order to reproduce the SNR's observed size, expansion rate
and thermal X-ray emission we employ a piecewise homogeneous model for the
progenitor's circumstellar medium developed by
Borkowski et al. (1996).
It consists of a tenuous inner wind bubble, a dense shell of swept-up red
supergiant wind material, and a subsequent red supergiant wind region. A
quite large SNR interior magnetic field 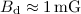 is required
to give a good fit for the radio and X-ray synchrotron emission. The steep
radio spectrum is consistent with efficient proton acceleration which
produces a significant shock modification and leads to a steep electron
spectrum at energies
is required
to give a good fit for the radio and X-ray synchrotron emission. The steep
radio spectrum is consistent with efficient proton acceleration which
produces a significant shock modification and leads to a steep electron
spectrum at energies 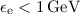 . The calculated integral
γ-ray flux from Cas A,
. The calculated integral
γ-ray flux from Cas A, 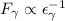 ,
is dominated by
,
is dominated by 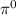 -decay γ-rays due to relativistic protons.
It extends up to roughly
-decay γ-rays due to relativistic protons.
It extends up to roughly 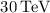 if CR diffusion is as strong as the Bohm
limit. At TeV energies it satisfactorily agrees with the value
if CR diffusion is as strong as the Bohm
limit. At TeV energies it satisfactorily agrees with the value
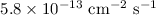 detected by the HEGRA collaboration.
detected by the HEGRA collaboration.
Key words: supernovae: individual: Cassiopeia A / cosmic rays / gamma rays: theory / acceleration of particles / shock waves / radiation mechanisms: non-thermal
© ESO, 2003
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


