| Issue |
A&A
Volume 400, Number 1, March II 2003
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 279 - 291 | |
| Section | Stellar structure and evolution | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20021908 | |
| Published online | 24 February 2003 | |
Long-term spectroscopic monitoring of the Luminous Blue Variable HD 160529*
1
Landessternwarte Königstuhl, 69117 Heidelberg, Germany
2
L-3 Communications, NASA/GSFC, Greenbelt, MD 20771, USA
3
Astronomy Group, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Pleinlan 2, 1050 Brussels, Belgium
4
European Southern Observatory, 85748 Garching, Karl-Schwarzschild-Str. 2, Germany
Corresponding author: O. Stahl, O.Stahl@lsw.uni-heidelberg.de
Received:
7
November
2002
Accepted:
19
December
2002
We have spectroscopically monitored the galactic Luminous
Blue Variable HD 160529 and obtained an extensive high-resolution
data set that covers the years 1991 to 2002. During this period, the
star evolved from an extended photometric minimum phase towards a new
visual maximum. In several observing seasons, we covered up to four
months with almost daily spectra. Our spectra typically cover most of
the visual spectral range with a high spectral resolution
(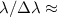 20 000 or more). This allows us to
investigate the variability in many lines and on many time scales from
days to years. We find a correlation between the photospheric
Hei lines and the brightness of the star, both on a time scale
of months and on a time scale of years. The short-term variations are
smaller and do not follow the long-term trend, strongly suggesting
different physical mechanisms. Metal lines also show both short-term
and long-term variations in strength and also a long-term trend in
radial velocity. Most of the line-profile variations can be attributed
to changing strengths of lines. Propagating features in the line
profiles are rarely observed. We find that the mass-loss rate of
HD 160529 is almost independent of temperature, i.e. visual
brightness.
20 000 or more). This allows us to
investigate the variability in many lines and on many time scales from
days to years. We find a correlation between the photospheric
Hei lines and the brightness of the star, both on a time scale
of months and on a time scale of years. The short-term variations are
smaller and do not follow the long-term trend, strongly suggesting
different physical mechanisms. Metal lines also show both short-term
and long-term variations in strength and also a long-term trend in
radial velocity. Most of the line-profile variations can be attributed
to changing strengths of lines. Propagating features in the line
profiles are rarely observed. We find that the mass-loss rate of
HD 160529 is almost independent of temperature, i.e. visual
brightness.
Key words: stars: individual: HD 160529 / stars: early-type / stars: emission-line, Be / stars: variables: general / stars: mass-loss
© ESO, 2003
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


