| Issue |
A&A
Volume 399, Number 3, March I 2003
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 1109 - 1114 | |
| Section | Stellar structure and evolution | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20021747 | |
| Published online | 14 February 2003 | |
The thermal radiation of the isolated neutron star RX J1856.5–3754 observed with Chandra and XMM-Newton
Max-Planck-Institut für extraterrestrische Physik, PO Box 1312, 85741 Garching, Germany
Corresponding author: V. Burwitz, burwitz@mpe.mpg.de
Received:
24
October
2002
Accepted:
21
November
2002
We present results of the analysis of data collected in 57-ks XMM-Newton
and 505-ks Chandra observations of the nearby ( 120 pc) isolated
neutron star RX J1856.5–3754. We confirm most of the statements made by
Burwitz et al. (2001) who discussed the original 55-ks Chandra
data. Detailed spectral analysis of the combined X-ray and optical data rules
out the currently available nonmagnetic light and heavy element neutron star
atmosphere (LTE) models with hydrogen, helium, iron and solar compositions.
We find that strongly magnetized atmosphere models also are unable to represent
the data. The X-ray and optical data show no spectral features and are best
fitted with a two-component blackbody model with
120 pc) isolated
neutron star RX J1856.5–3754. We confirm most of the statements made by
Burwitz et al. (2001) who discussed the original 55-ks Chandra
data. Detailed spectral analysis of the combined X-ray and optical data rules
out the currently available nonmagnetic light and heavy element neutron star
atmosphere (LTE) models with hydrogen, helium, iron and solar compositions.
We find that strongly magnetized atmosphere models also are unable to represent
the data. The X-ray and optical data show no spectral features and are best
fitted with a two-component blackbody model with
 eV
and
eV
and 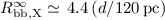 km
for the hot X-ray emitting region, and
km
for the hot X-ray emitting region, and 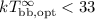 eV
and
eV
and 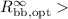 17 (d/120 pc) km for
the rest of the neutron star surface responsible for the optical flux.
The large number of counts collected with XMM-Newton allows us to
reduce the upper limit on periodic variation in the X-ray range down to
1.3% (at a 2σ confidence level) in the
17 (d/120 pc) km for
the rest of the neutron star surface responsible for the optical flux.
The large number of counts collected with XMM-Newton allows us to
reduce the upper limit on periodic variation in the X-ray range down to
1.3% (at a 2σ confidence level) in the  Hz frequency
range. In an attempt to explain this small variability, we discuss an
one-component model with
Hz frequency
range. In an attempt to explain this small variability, we discuss an
one-component model with 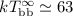 eV and
eV and
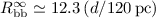 km.
This model requires a low radiative efficiency in the X-ray domain, which may
be expected if the neutron star has a condensed matter surface.
km.
This model requires a low radiative efficiency in the X-ray domain, which may
be expected if the neutron star has a condensed matter surface.
Key words: stars: atmospheres / stars: individual: RX J1856.5–3754 / stars: neutron / X-rays: stars
© ESO, 2003
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


