| Issue |
A&A
Volume 399, Number 1, February III 2003
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 337 - 342 | |
| Section | Celestial mechanics and astrometry | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20021785 | |
| Published online | 05 February 2003 | |
Testing general relativity by micro-arcsecond global astrometry
1
Istituto di Fisica “G. Galilei”, Via Marzolo 8, 35100 Padova, Italy
2
Istituto Nazionale di Fisica Nucleare (INFN), Sezione di Padova
3
Centro per gli Studi e le Attività Spaziali “G. Colombo” (CISAS), Padova
4
INAF, Osservatorio Astronomico di Torino, 10025 Pino Torinese TO, Italy
Corresponding author: M. G. Lattanzi, lattanzi@to.astro.it
Received:
24
October
2002
Accepted:
27
November
2002
The global astrometric observations of a GAIA-like
satellite were modeled within the PPN formulation of
Post-Newtonian gravitation. An extensive experimental campaign
based on realistic end-to-end simulations was conducted to
establish the sensitivity of global astrometry to the PPN
parameter γ, which measures the amount of space curvature
produced by unit rest mass. The results show that, with just a few
thousands of relatively bright, photometrically stable, and
astrometrically well behaved single stars, among the ~109 objects that will be observed by GAIA, γ can be estimated
after 1 year of continuous observations with an accuracy of
~10-5 at the 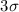 level. Extrapolation to the full 5-year mission
of these results based on the scaling properties of the adjustment procedure
utilized suggests that the accuracy of
level. Extrapolation to the full 5-year mission
of these results based on the scaling properties of the adjustment procedure
utilized suggests that the accuracy of 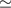
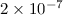 , at the same
, at the same 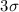 level,
can be reached with ~ 106 single stars, again chosen as the most astrometrically stable
among the millions available in the magnitude range
level,
can be reached with ~ 106 single stars, again chosen as the most astrometrically stable
among the millions available in the magnitude range 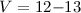 .
These accuracies compare quite favorably with recent findings of scalar-tensor
cosmological models, which predict for γ a present-time
deviation,
.
These accuracies compare quite favorably with recent findings of scalar-tensor
cosmological models, which predict for γ a present-time
deviation, 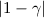 , from the General
Relativity value between 10-5 and 10-7 .
, from the General
Relativity value between 10-5 and 10-7 .
Key words: astrometry / relativity / gravitation / space vehicles: instruments
© ESO, 2003
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


