| Issue |
A&A
Volume 398, Number 1, January IV 2003
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 297 - 303 | |
| Section | The Sun | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20021616 | |
| Published online | 14 January 2003 | |
Inversion of the intensity-magnetic field relationship in solar active regions
1
Space Science & Technology Department, Rutherford Appleton Laboratory, Chilton, Didcot, Oxfordshire, OX11 0QX, UK
2
L-3 Communications/EER Systems Inc., NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD 20771, USA
Corresponding author: A. Fludra, A.Fludra@rl.ac.uk
Received:
6
June
2002
Accepted:
4
November
2002
We discuss the relationship between the EUV spectral line
intensities and the photospheric magnetic flux in solar active
regions. Since the histograms of the magnetic flux density in active
region plages can be approximated by an exponential function, the
equation describing how the observed total line intensity integrated
over an active region area arises from the magnetic field, can be
approximated by a Laplace integral. We use this property to solve an
inverse problem and derive a function relating the line intensity from
individual loops to the photospheric magnetic flux density at their
footpoints. We propose a simple model in which the intensity of a
coronal line Fe XVI 360.8 Å in an individual coronal loop is
proportional to the footpoint magnetic flux density to the power of
δ and explore how well the value of δ is constrained by
the observations. Using EUV spectra from the Coronal Diagnostic
Spectrometer (CDS) on SOHO and magnetograms from SOHO Michelson
Doppler Imager for 26 active regions without sunspots, we find that
the value of δ depends on the magnetic flux density threshold
used to define active region magnetic area. When even the weakest
fields are included, we obtain 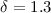 , where
, where 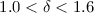 with 90% confidence. This result can be used to provide constraints on coronal
heating models.
with 90% confidence. This result can be used to provide constraints on coronal
heating models.
Key words: Sun: magnetic field / Sun: corona / Sun: UV radiation
© ESO, 2003
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


