| Issue |
A&A
Volume 376, Number 2, September II 2001
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 713 - 726 | |
| Section | Astronomical instrumentation | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20011041 | |
| Published online | 15 September 2001 | |
Magnetoconvection and dynamo coefficients:
Dependence of the α effect on rotation and magnetic field
1
Kiepenheuer-Institut für Sonnenphysik, Schöneckstraße 6, 79104 Freiburg, Germany
2
Department of Mathematics, University of Newcastle upon Tyne, NE1 7RU, UK
3
Nordita, Blegdamsvej 17, 2100 Copenhagen Ø, Denmark
Corresponding author: M. Stix, stix@kis.uni-freiburg.de
Received:
24
October
2000
Accepted:
12
July
2001
We present numerical simulations of three-dimensional compressible magnetoconvection
in a rotating rectangular box that represents a section of the solar convection zone.
The box contains a convectively unstable layer, surrounded by stably
stratified layers with overshooting convection. The magnetic Reynolds number,
Rm, is chosen subcritical, thus excluding spontaneous growth of the magnetic
field through dynamo action, and the magnetic energy is maintained by
introducing a constant magnetic field into the box, once convection has attained
a statistically stationary state. Under the influence of the Coriolis force,
the advection of the magnetic field results in
a non-vanishing contribution to the mean electric
field, given by 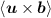 . From this electric field, we calculate
the α-effect, separately for the stably and the unstably stratified
layers, by averaging over time and over suitably defined volumes. From the
variation of α we derive an error estimate, and the dependence of
α on rotation and magnetic field strength is studied. Evidence is
found for rotational quenching of the vertical
α effect, and
for a monotonic increase of the horizontal
α effect with
increasing rotation. For
. From this electric field, we calculate
the α-effect, separately for the stably and the unstably stratified
layers, by averaging over time and over suitably defined volumes. From the
variation of α we derive an error estimate, and the dependence of
α on rotation and magnetic field strength is studied. Evidence is
found for rotational quenching of the vertical
α effect, and
for a monotonic increase of the horizontal
α effect with
increasing rotation. For 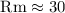 , our results for both
vertical and horizontal α effect are consistent with magnetic
quenching by a factor
, our results for both
vertical and horizontal α effect are consistent with magnetic
quenching by a factor ![$[1+{\rm Rm} (B_0/B_{\rm eq})^2]^{-1}$](/articles/aa/abs/2001/35/aa10386/aa10386_tex_eq3.png) . The signs
of the small-scale current helicity and of the vertical component of
α are found to be opposite to those for isotropic turbulence.
. The signs
of the small-scale current helicity and of the vertical component of
α are found to be opposite to those for isotropic turbulence.
Key words: convection / magnetic fields
© ESO, 2001
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


