| Issue |
A&A
Volume 374, Number 2, August I 2001
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 588 - 598 | |
| Section | Interstellar and circumstellar matter | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20010695 | |
| Published online | 15 August 2001 | |
System parameters of the long-period polar V1309 Ori*
Astrophysikalisches Institut Potsdam, An der Sternwarte 16, 14482 Potsdam, Germany
Corresponding author: A. Staude, astaude@aip.de
Received:
15
February
2001
Accepted:
10
May
2001
Based on high-resolution optical spectroscopy in the blue and the
near infra-red spectral range, we derived velocity images (Doppler
tomograms) of the mass-donating secondary star and the accretion
stream of the long-period eclipsing polar V1309 Ori (RX J0515.41+0104.6).
Combined with HST-spectroscopy of high time resolution and optical
photometry we were able to derive the main system parameters
and to determine the accretion geometry of the binary. The
length of the eclipse of the white dwarf is 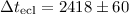 s,
the mass ratio
s,
the mass ratio 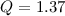 -1.63, and the orbital inclination
-1.63, and the orbital inclination 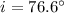 -
-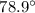 . The surface of the secondary star could be resolved in
the Doppler image of NaI absorption lines, where it shows a marked
depletion on the X-ray irradiated side. The accretion
geometry proposed by us with a nearly aligned rotator, co-latitude
. The surface of the secondary star could be resolved in
the Doppler image of NaI absorption lines, where it shows a marked
depletion on the X-ray irradiated side. The accretion
geometry proposed by us with a nearly aligned rotator, co-latitude
 ,
tilted away from the ballistic stream, azimuth
,
tilted away from the ballistic stream, azimuth 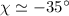 ,
explains the shape of the emission-line Doppler tomograms and the shape
of optical/UV eclipse light curves.
,
explains the shape of the emission-line Doppler tomograms and the shape
of optical/UV eclipse light curves.
Key words: accretion / stars: binaries: eclipsing / stars: individual: V1309 Ori / stars: magnetic fields / stars: novae / cataclysmic variables
© ESO, 2001
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


