| Issue |
A&A
Volume 374, Number 2, August I 2001
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 615 - 628 | |
| Section | Interstellar and circumstellar matter | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20010726 | |
| Published online | 15 August 2001 | |
Time-resolved spectroscopy of the roAp star γ Equ *
1
Uppsala Astronomical Observatory, Box 515, 751 20 Uppsala, Sweden
2
Institute of Astronomy, Russian Academy of Sciences, Pyatnitskaya 48, 109017 Moscow, Russia e-mail: ryabchik@inasan.rssi.ru
3
Institute for Astronomy, University of Vienna, Türkenschanzstrasse 17, 1180 Vienna, Austria e-mail: ryabchik@tycho.astro.univie.ac.at
Corresponding author: O. Kochukhov, oleg@astro.uu.se
Received:
7
December
2000
Accepted:
17
May
2001
We report results of the spectroscopic monitoring
of the roAp star γ Equ with the ESO 3.6-m telescope. During 1.5 hours of
observations a series of very high-resolution and high 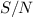 spectra was obtained for this star
in the 6138-6165 Åspectral region. Short exposure times allowed us
to resolve changes of γ Equ line profiles due to the rapid pulsations
and to follow profile variations over 5 oscillation cycles. From this unique
observational material information on amplitudes and phase shifts of
radial velocity (RV) variations was extracted for 29 lines of 17 individual ions.
We confirmed that spectral lines of rare-earth elements (REE) have
the largest pulsation amplitudes, reaching up to 0.8 km s-1. Moreover, we
detected a phase shift between RV variations of singly and doubly ionized
REE, discovered significant RV shifts of weak Nai
lines and analysed line profile variations of Priii and Ndiii spectral features.
This rich observational material opens a
possibility to obtain a detailed picture of the vertical stratification of
chemical elements and extract the main characteristics of the pulsational mode(s).
In our observations we did not find support for the existence of the unique
dependence of RV amplitude
on line strength suggested in earlier spectroscopic studies of roAp stars. Instead,
we argue that the individuality of the variations of all ions is a result of
the complex interplay between inhomogeneous vertical and horizontal distributions
of chemical elements and individual pulsation modes of γ Equ.
We show that the extra line broadening observed in γ Equ spectrum is most likely caused by pulsations.
A detailed analysis of Priii and Ndiii line profile variations resulted in the
estimate of
spectra was obtained for this star
in the 6138-6165 Åspectral region. Short exposure times allowed us
to resolve changes of γ Equ line profiles due to the rapid pulsations
and to follow profile variations over 5 oscillation cycles. From this unique
observational material information on amplitudes and phase shifts of
radial velocity (RV) variations was extracted for 29 lines of 17 individual ions.
We confirmed that spectral lines of rare-earth elements (REE) have
the largest pulsation amplitudes, reaching up to 0.8 km s-1. Moreover, we
detected a phase shift between RV variations of singly and doubly ionized
REE, discovered significant RV shifts of weak Nai
lines and analysed line profile variations of Priii and Ndiii spectral features.
This rich observational material opens a
possibility to obtain a detailed picture of the vertical stratification of
chemical elements and extract the main characteristics of the pulsational mode(s).
In our observations we did not find support for the existence of the unique
dependence of RV amplitude
on line strength suggested in earlier spectroscopic studies of roAp stars. Instead,
we argue that the individuality of the variations of all ions is a result of
the complex interplay between inhomogeneous vertical and horizontal distributions
of chemical elements and individual pulsation modes of γ Equ.
We show that the extra line broadening observed in γ Equ spectrum is most likely caused by pulsations.
A detailed analysis of Priii and Ndiii line profile variations resulted in the
estimate of 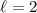 or 3,
or 3, 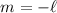 or
or 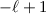 and
and 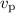
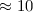 km s-1 for the p-mode of the
main pulsation frequency.
km s-1 for the p-mode of the
main pulsation frequency.
Key words: stars: chemically peculiar / stars: oscillations / stars: individual: γ Equ
© ESO, 2001
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


