| Issue |
A&A
Volume 425, Number 2, October II 2004
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 641 - 648 | |
| Section | Stellar structure and evolution | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20040558 | |
| Published online | 21 September 2004 | |
Balmer lines as T and log
g indicators for non-solar composition
atmospheres*
and log
g indicators for non-solar composition
atmospheres*
An application to the extremely helium-weak star HR 6000
1
INAF - Catania Astrophysical Observatory, via S. Sofia 78, 95123 Catania, Italy e-mail: [gcatanzaro;fleone]@ct.astro.it
2
European Southern Observatory, Casilla 19001, Santiago 19, Chile e-mail: tdall@eso.org
Received:
30
March
2004
Accepted:
11
June
2004
Although the importance of a correct abundance assumption
in the determination of effective temperature and surface gravity of a star has been demonstrated
in the literature, this determination is often still extremely simplified, neglecting the effects
of non-solar chemical abundances. In this paper we show how the modeling of the profiles of
H and H
and H , commonly used as Teff and
, commonly used as Teff and 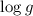 indicators, is affected
when the chemical composition is far from the standard one.
As a target for our study we selected the chemically peculiar star HR 6000. Comparing
the observed and synthetic profiles of H
indicators, is affected
when the chemical composition is far from the standard one.
As a target for our study we selected the chemically peculiar star HR 6000. Comparing
the observed and synthetic profiles of H and H
and H we obtained
Teff = 12 950 K and
we obtained
Teff = 12 950 K and 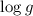 = 4.05; the atmospheric model has been computed with
a metal opacity scale evaluated for [M/H] = -0.5 and He/H = 0. A number of FeII lines
have been
used to infer the rotational velocity (
= 4.05; the atmospheric model has been computed with
a metal opacity scale evaluated for [M/H] = -0.5 and He/H = 0. A number of FeII lines
have been
used to infer the rotational velocity (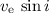 = 0 km s-1) and the heliocentric radial
velocity (
= 0 km s-1) and the heliocentric radial
velocity (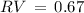 km s-1). By requiring that the abundance of iron is independent of the 96
measured equivalent widths, we determined the microturubulence velocity (
km s-1). By requiring that the abundance of iron is independent of the 96
measured equivalent widths, we determined the microturubulence velocity ( km s-1).
The abundance pattern coming
from our study is similar to the one inferred from UV lines by Castelli et al. ([CITE]),
with the exception of O, Al, Si, Sc and Ni. Possible causes for these descrepancies are discussed.
With respect to the Sun, we found the iron peak elements to be normal or overabundant and
the light elements, with the
exception of Na and P, to be extremely underabundant.
We find that HR 6000 is one of the most He-underabundant among the chemically peculiar stars.
km s-1).
The abundance pattern coming
from our study is similar to the one inferred from UV lines by Castelli et al. ([CITE]),
with the exception of O, Al, Si, Sc and Ni. Possible causes for these descrepancies are discussed.
With respect to the Sun, we found the iron peak elements to be normal or overabundant and
the light elements, with the
exception of Na and P, to be extremely underabundant.
We find that HR 6000 is one of the most He-underabundant among the chemically peculiar stars.
Key words: stars: fundamental parameters / stars: individual: HR 6000 / stars: chemically peculiar / stars: atmospheres / stars: abundances
© ESO, 2004
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


