| Issue |
A&A
Volume 420, Number 1, June II 2004
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Page(s) | 343 - 350 | |
| Section | The Sun | |
| DOI | https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361:20034247 | |
| Published online | 14 May 2004 | |
Solar energetic particle event onset as analyzed from simulated data
Department of Physical Sciences, PO Box 64, 00014 University of Helsinki, Finland
Corresponding author: R. Vainio, rami.vainio@helsinki.fi
Received:
1
September
2003
Accepted:
25
February
2004
Solar energetic particle (SEP) event onset is analyzed using
simulated data. A large number of simulations using different coronal and
interplanetary (IP) scattering conditions are performed. Protons in
the energy range of 0.13–57 MeV are considered. The simulated data
are analyzed employing a velocity dispersion analysis (VDA) to the
proton-flux onset times in 16 energy channels. As a result of the
analysis, the apparent coronal release time, t0, and the apparent
IP path length, s, of the first-observed particles are obtained. It
is shown that typical IP scattering conditions, i.e., 1-GV radial mean
free path of 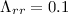 –1 AU with a
–1 AU with a 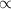
 rigidity dependence, lead to apparent path lengths of
rigidity dependence, lead to apparent path lengths of 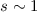 –2 AU,
consistent with observations. Thus, SEP events with
–2 AU,
consistent with observations. Thus, SEP events with  AU can
simply be explained as a result of IP scattering. Models with coronal
mean free paths small enough to enable proton acceleration to high
energies in quasi-parallel shocks close to the Sun are shown to yield
VDA results in agreement with observations, at least with
AU can
simply be explained as a result of IP scattering. Models with coronal
mean free paths small enough to enable proton acceleration to high
energies in quasi-parallel shocks close to the Sun are shown to yield
VDA results in agreement with observations, at least with  . As a result of IP scattering, the inaccuracy of the
release times is tens of minutes in events with
. As a result of IP scattering, the inaccuracy of the
release times is tens of minutes in events with 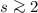 AU, which
may prevent accurate timing of particle release using the VDA method
in such events. Low contrast between the time-of-maximum intensity of
the studied SEP event and the pre-event background intensity and/or a
large difference between the forms of the respective energy spectra
may also lead to errors in derived onset times. Best timing results
(with errors typically less than 10 min) are obtained for large IP mean free paths,
AU, which
may prevent accurate timing of particle release using the VDA method
in such events. Low contrast between the time-of-maximum intensity of
the studied SEP event and the pre-event background intensity and/or a
large difference between the forms of the respective energy spectra
may also lead to errors in derived onset times. Best timing results
(with errors typically less than 10 min) are obtained for large IP mean free paths, 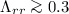 AU (typically resulting in
small values of
AU (typically resulting in
small values of  AU), and large intensity contrast
between the SEP event and the pre-event background.
AU), and large intensity contrast
between the SEP event and the pre-event background.
Key words: Sun: particle emission / Sun: coronal mass ejections (CMEs) / Sun: flares / Sun: solar wind / turbulence
© ESO, 2004
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


