Dust reverberation-mapping of the Seyfert 1 galaxy WPVS48 (Pozo Nunez et al.)
- Details
- Published on 09 January 2014
Vol. 561
In section 1. Letters
Dust reverberation-mapping of the Seyfert 1 galaxy WPVS48
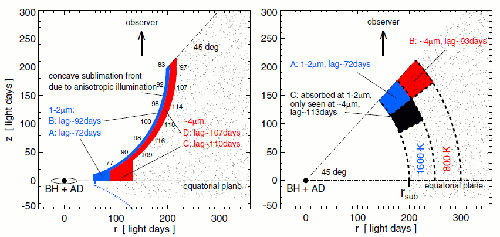 Active galaxy nuclei (AGN) are thought to be composed of an accretion disk (AD) around a supermassive black hole, surrounded by a broad line region (BLR) and a dusty torus. The variable continuum emission from the AD is reflected by the BLR and torus with a time delay, directly yielding the sizes of the regions that otherwise would not be resolved: this is the reverberation-mapping technique.
Using robotic telescopes in Chile, the authors used this technique on the z=0.0377 Seyfert 1 galaxy WPVS48 with surprising results: the light curves in the optical and near-infrared (NIR) revealed unexpected variations. The NIR, tracing the hot (∼1600 K) dust echo, lags the optical variations by about 70 days, three times shorter than expected from the dust sublimation radius inferred from the optical-UV luminosity. Two potential scenarios are discussed in which the torus either comes closer to the AD or closer to the observer. Longer-wavelength dust reverberation data might enable one to distinguish between the two scenarios.
Active galaxy nuclei (AGN) are thought to be composed of an accretion disk (AD) around a supermassive black hole, surrounded by a broad line region (BLR) and a dusty torus. The variable continuum emission from the AD is reflected by the BLR and torus with a time delay, directly yielding the sizes of the regions that otherwise would not be resolved: this is the reverberation-mapping technique.
Using robotic telescopes in Chile, the authors used this technique on the z=0.0377 Seyfert 1 galaxy WPVS48 with surprising results: the light curves in the optical and near-infrared (NIR) revealed unexpected variations. The NIR, tracing the hot (∼1600 K) dust echo, lags the optical variations by about 70 days, three times shorter than expected from the dust sublimation radius inferred from the optical-UV luminosity. Two potential scenarios are discussed in which the torus either comes closer to the AD or closer to the observer. Longer-wavelength dust reverberation data might enable one to distinguish between the two scenarios.

