Fig. 5
Download original image
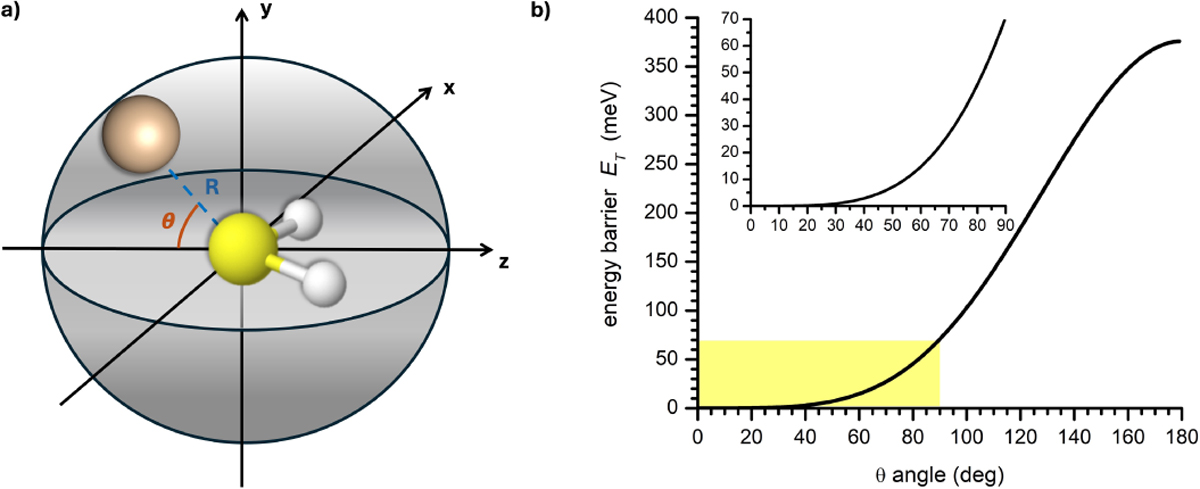
a) Schematic representation of the Si+−H2S reactive system. The H2S molecule is bound within the xz plane, while the Si+ ion moves within the yz plane, at a fixed distance from the molecule (i.e. the equilibrium Si-S bond length R = 3.8 Å) and with an angle, θ, with respect to the xz plane. As the ion moves, it probes the electrostatic potential from z = −R to z = +R. b) Energy barrier (ET) as a function of θ: the electrostatic potential increases as the ion moves from θ = 0° to 180° in the yz plane, with an increase of the repulsive contribution given by the hydrogen atoms. The barrier is obtained as a difference between the effective potential calculated at θ = θ′ and θ = 0°. The inset is an expansion of the yellow area in the main graph.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


