Table 1
Removal of systematic noise with PCA.
| Algorithm | Data type | R | Usage of PCA | Features | Samples | Forward Model | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADI + PCA/KLIP | Imaging | – | Full PSF | X × Y | T | (1), (2) | |
| TRAP | Imaging | – | Full PSF | T | X × Y | ✔ | (3) |
| PCA-Temporal | Imaging | – | Full PSF | T | X × Y | (4) | |
| ASDI/CODI | IFS | <1000 | Full PSF | X × Y | Λ × T | (5) | |
| FMMF | IFS | <1000 | Full PSF | X × Y | Λ × T | ✔ | (6) |
| HRSDI | IFS | >1000 | Residual systematics | Λ | X × Y | (7), (8), (9) | |
| Ruffio and Hoch | IFS | >1000 | Residual systematics | 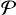 × Λ × Λ |
X × Y | ✔ | (10), (11) |
| Spectral PCA | IFS | >1000 | Full PSF | Λ | X × Y | This work | |
Notes. Overview of application schemes for PCA-based systematic noise subtraction. Depending on the scheme and data type, PCA can be applied along different dimensions: the letters X and Y denote the two spatial axes, T is the time axis, Λ is the spectral axis, and  is a local 5 × 5 patch in space. The column R denotes the spectral resolution. In the last three rows, i.e. for the methods HRSDI, Ruffio and Hoch, and Spectral PCA, the column “Usage of PCA” refers to the steps (i) and (ii) described in the main text. References: (1) Amara & Quanz (2012), (2) Soummer et al. (2012), (3) Samland et al. (2021), (4) Long et al. (2023), (5) Kiefer et al. (2021), (6) Ruffio et al. (2017), (7) Hoeijmakers et al. (2018), (8) Haffert et al. (2019), (9) Cugno et al. (2021), (10) Hoch et al. (2020), (11) Ruffio et al. (2021).
is a local 5 × 5 patch in space. The column R denotes the spectral resolution. In the last three rows, i.e. for the methods HRSDI, Ruffio and Hoch, and Spectral PCA, the column “Usage of PCA” refers to the steps (i) and (ii) described in the main text. References: (1) Amara & Quanz (2012), (2) Soummer et al. (2012), (3) Samland et al. (2021), (4) Long et al. (2023), (5) Kiefer et al. (2021), (6) Ruffio et al. (2017), (7) Hoeijmakers et al. (2018), (8) Haffert et al. (2019), (9) Cugno et al. (2021), (10) Hoch et al. (2020), (11) Ruffio et al. (2021).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


