Fig. 3.
Download original image
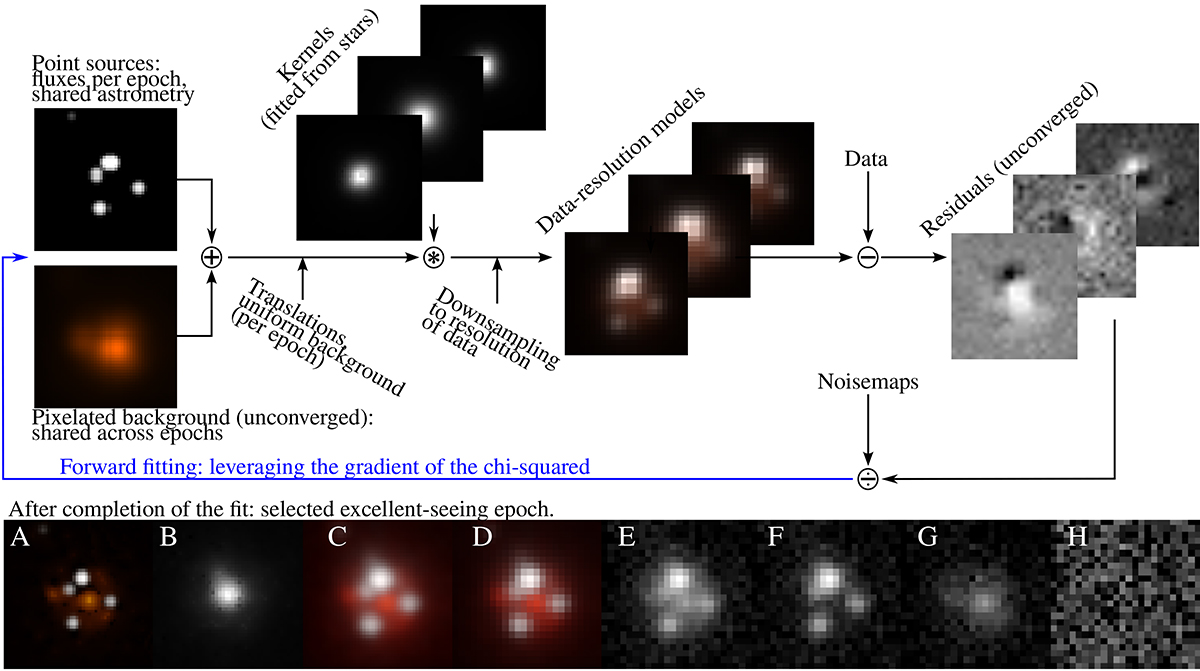
Overview of the final step of light curve extraction: the forward-modelling of the lens cutouts. Note that the colour coding is only used to differentiate point-source and pixelated components of the models, and does not indicate observations in multiple filters. Top: Components of the forward-modelling process of the zero-point-calibrated cutouts, starting with a high-resolution model containing a fully tunable grid of pixels and point sources of tunable flux (added to the grid of pixels as two-pixel FWHM Gaussians). The model is degraded to the resolution of the data, and the residuals are minimised through gradient-based optimisation of the high resolution models. Bottom: Exploring the result of the forward modelling for a selected epoch. A is the fitted high-resolution model. B is the kernel, which transforms a point source in A into the PSF of the data. C is the convolution of A and B, which is then downsampled down to the pixel scale of the data, yielding D. A, C, and D have the background component in red and the point-source component in white. E is the data cutout. F and G are again the data, but with the background and point-source components subtracted, respectively. Finally, H shows the residuals upon subtraction of the two components from the data. This method allows for the precise determination of the astrometry of the point sources, reveals the morphology of the non-point source components at high resolution, and provides precise photometry unbiased by flux leakage between point source and non-point source components.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


