Fig. 10
Download original image
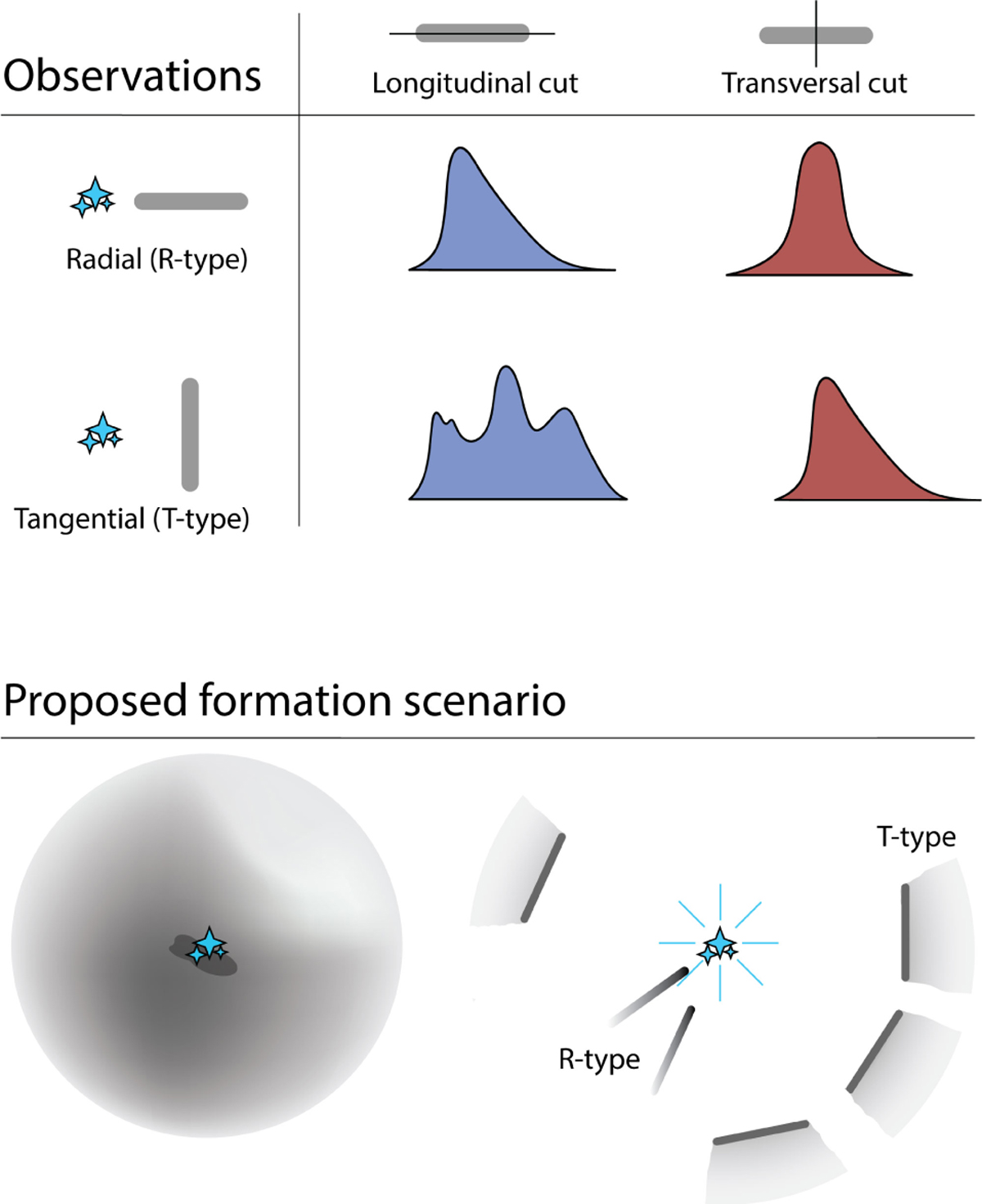
Top: summary of the longitudinal and transversal profile analysis. R-type profiles exhibit asymmetric longitudinal profiles and symmetric transversal profiles, whereas T-type profiles are characterized by generally flatter longitudinal profiles and asymmetric transversal profiles. These pronounced distinctions between the two filament types imply the existence of two separate mass assembly mechanisms. Bottom: a schematic representation of the proposed formation scenario. Variations in the initial gas distribution following the formation of massive stars may account for the emergence of the two filament types. T-type filaments could arise from a shell fragmentation process, while R-type filaments may result from the stretching and compression of denser gas in proximity to newly formed massive stars.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


