Fig. A.1
Download original image
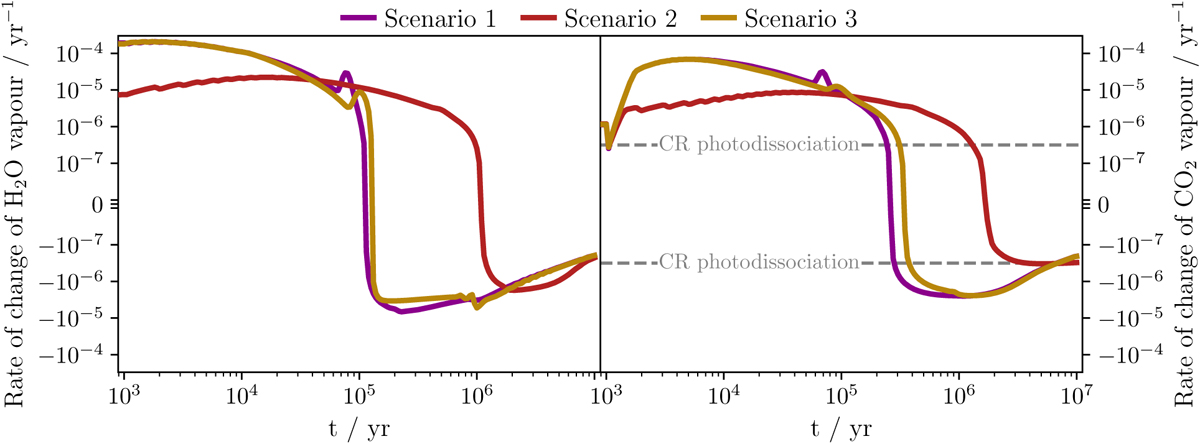
Evolution of the rate at which the vapour masses of H2O (left) and CO2 (right) are changing in a smooth disc model in Scenarios 1 (purple), 2 (gold), and 3 (red) as a result of delivery by drifting dust and viscous advection onto the star. A typical rate for cosmic ray (CR) photodissociation of CO2, 10−14 s−1, is shown as the dashed lines as a reference for the rates at which chemical reactions occur.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


