Fig. 11.
Download original image
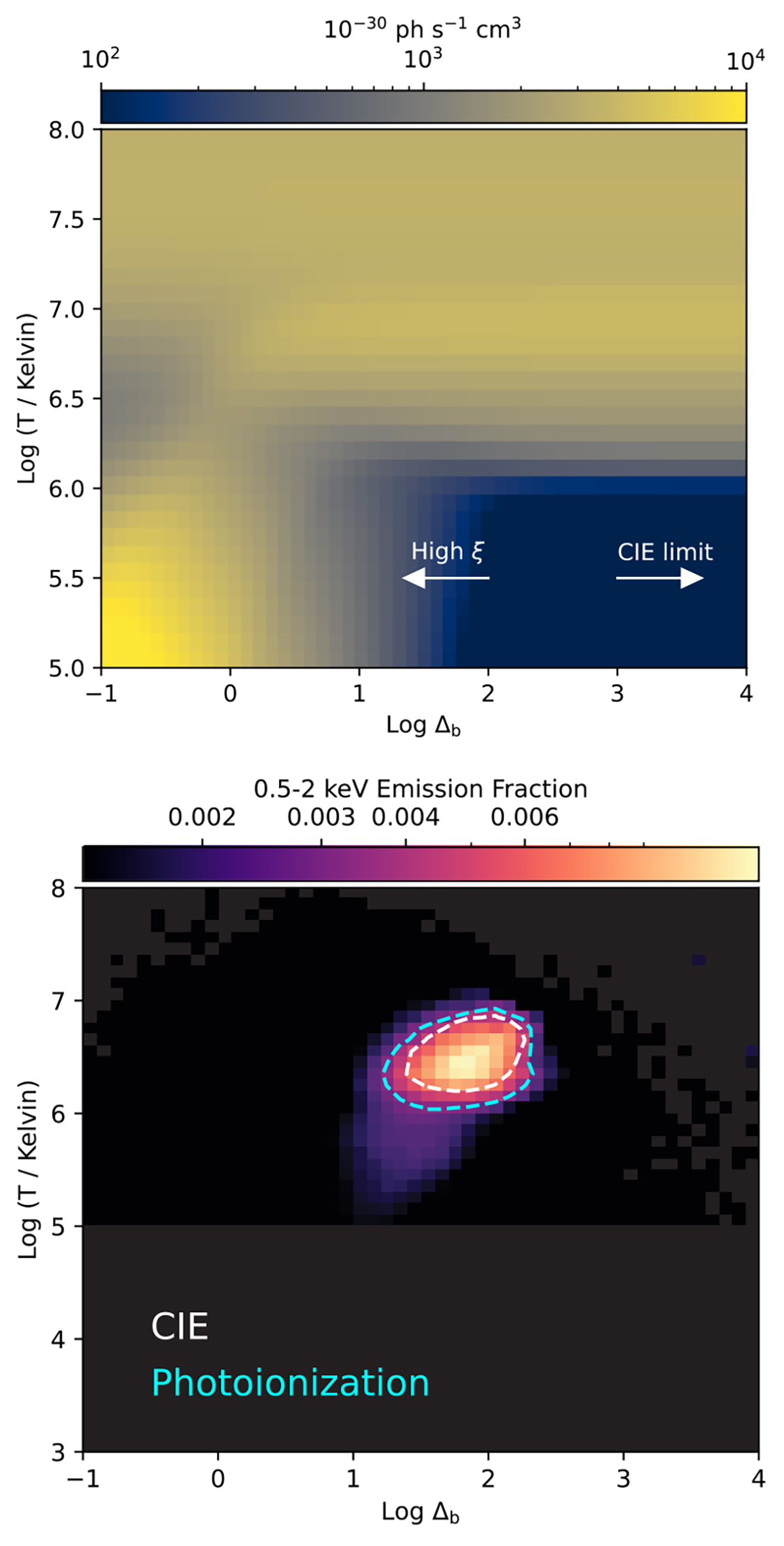
Impact of the cosmic UV background photoionization on the X-ray detectable phases. Top: Photon luminosity per unit of emission measure in the 0.5–2 keV band of the photoionized WHIM at different density (x-axis) and temperature (y-axis) by assuming Z = 0.2Z⊙. Towards the high density (low ionization parameter) end, the radiative cooling reaches the CIE limit and is simply a function of temperature. When Δb ≲ 1, the radiative cooling keeps high at low temperature. Bottom: Same as the right panel of Fig. 10 but calculated using the photoionization model. By taking the cosmic UV background photoionization into account, the size of the 50% enclosed phases contour is marginally larger than that of the CIE condition.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


