Fig. 8.
Download original image
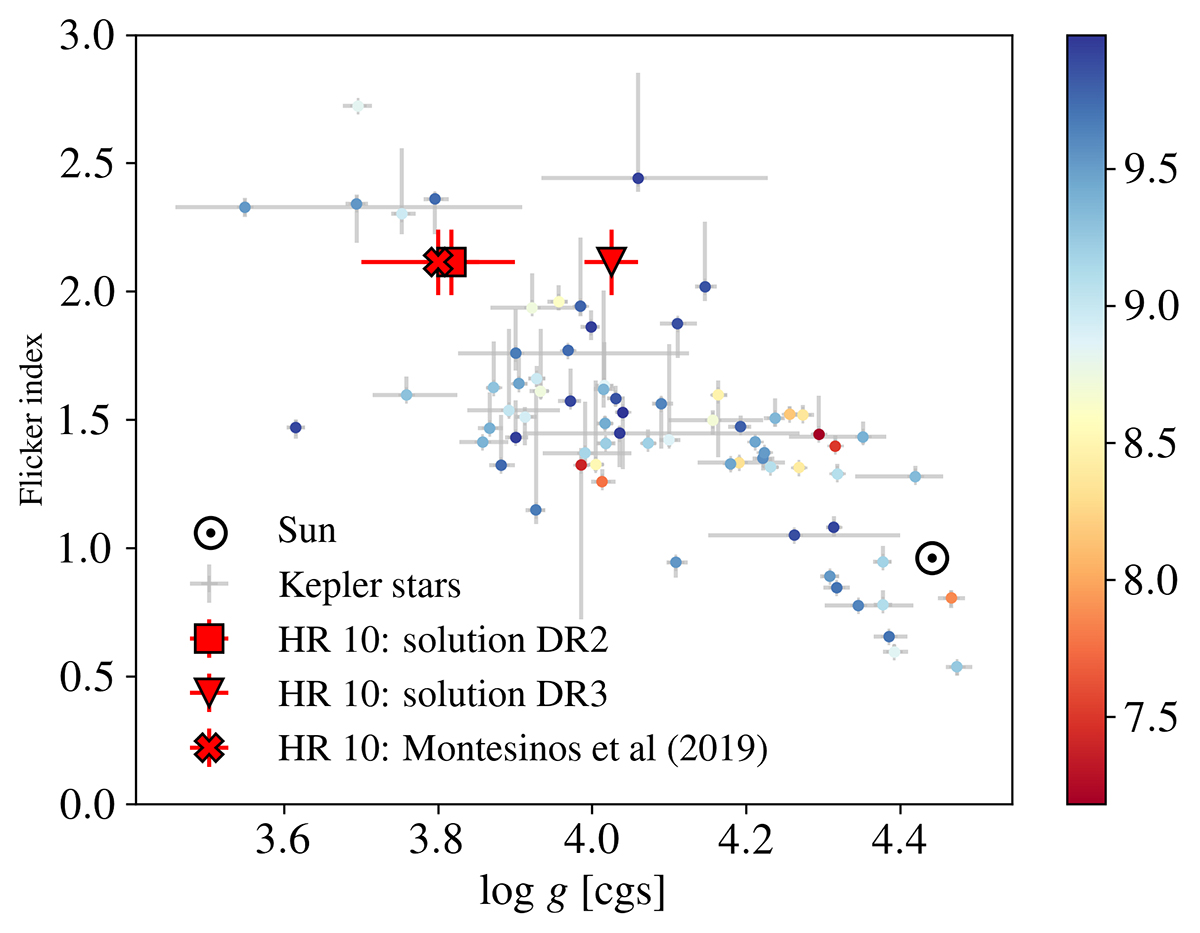
Estimated flicker indexes associated with granulation as a function of the stellar log g for Kepler bright (Kepler magnitude < 10) targets, adapted from Fig. 17 of Sulis et al. (2020). For this comparison, the flicker indexes have been interpolated to correspond to the value that would be measured at a constant level of high-frequency photon noise (here taken at 30 ppm). The quality of this interpolation depends on the level of photon noise, which is directly related to the stellar magnitude (indicated by the colour code). The flicker index inferred from solar VIRGO data (with a white Gaussian noise of 30 ppm standard deviation added) is shown with the solar symbol for reference. The flicker index inferred from HR 10 photometric data (no interpolation needed for this target; see footnote 7) is shown with the square, triangle, and cross symbols adopting log g from stellar modelling with Gaia DR2 data, Gaia DR3 data, and with spectroscopic analysis (M19), respectively (see Table 3).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


