Fig. 4.
Download original image
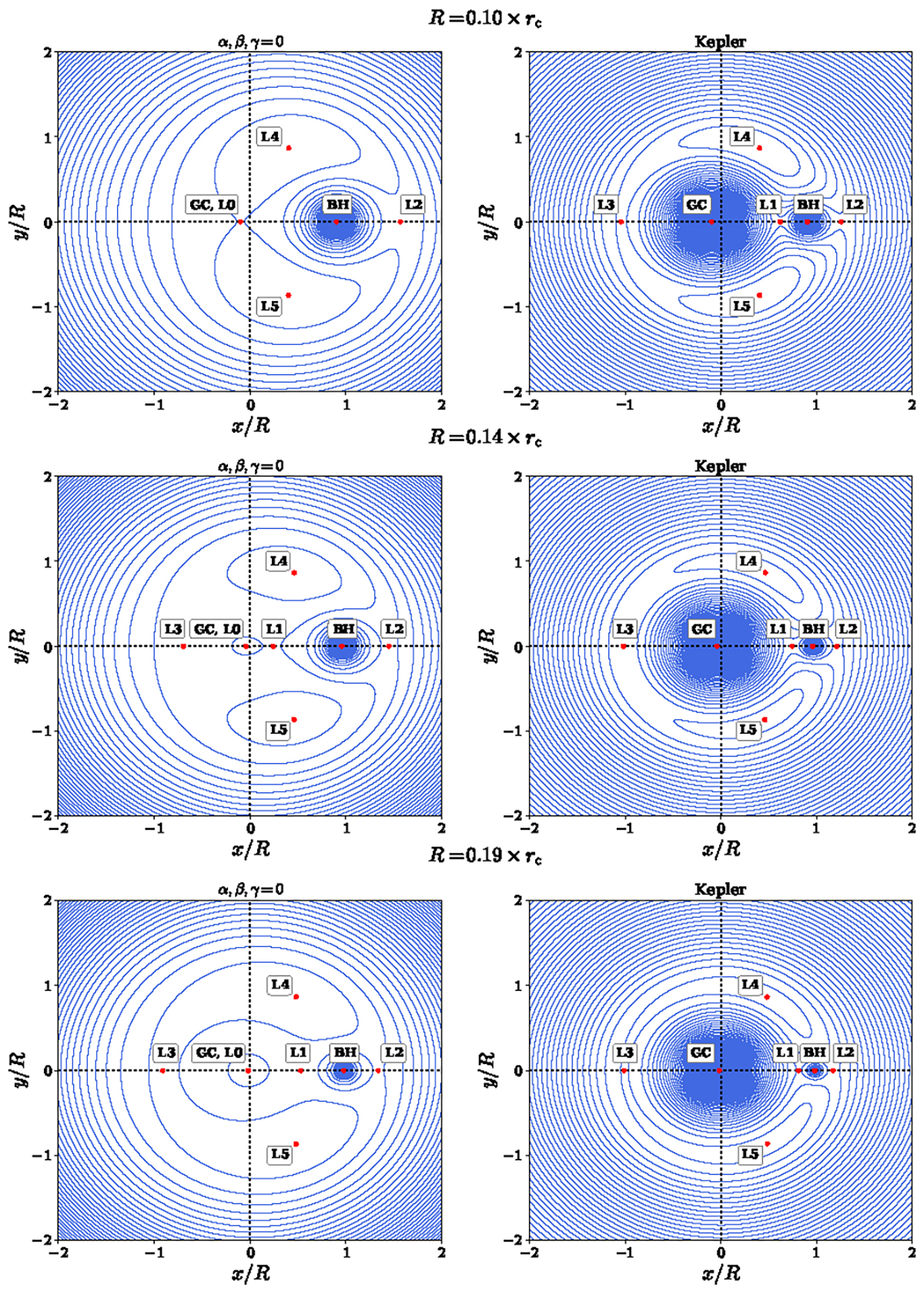
Effective potential of the galaxy + BH system plotted in the reference frame rotating at the angular frequency of the BH orbit in the (x, y) plane. The coordinates (x, y) = (0, 0) denote the center of mass, calculated for the sum of the BH mass and the mass of the host galaxy integrated up to the BH orbit. Hence the galactic center is shifted significantly from (0, 0) in some cases. The Lagrange points, along with the positions of the black hole (denoted BH) and galactic center (denoted GC), are highlighted in red. R = f × rc is the orbital radius of the BH, where f is a dimensionless factor and rc represents the core radius of the potential, defined by its inflection point. We observe distinct differences in the topology of the effective potential, as well as in the positioning and number of Lagrange points, between the cored galactic potential (on the left) and the Keplerian case (on the right) where we approximate the galaxy as a point mass equal to the enclosed galactic mass up to the BH orbit.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


