Fig. 3.
Download original image
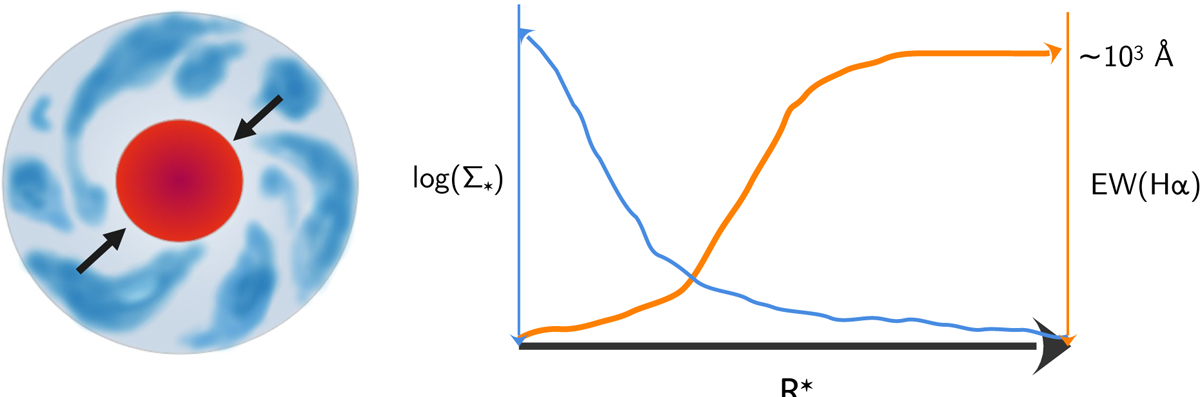
Schematic illustration of a high-z spiral galaxy in the early stages of its evolution. Massive SF clumps (blue) forming in the disk migrate inward and coalesce, promoting the growth of a high-stellar surface density Σ⋆ protobulge (e.g., Noguchi 1999; Bournaud et al. 2007; Mandelker et al. 2014). The rest-frame EW(Hα) of SF clumps, initially on the order of 103 Å (cf. Fig. A.7 and discussion in P22), decreases as they move inward, both because of their aging over the theoretically estimated migration timescale (τm = 0.6 − 1 Gyr) and because of the increasing line-of-sight dilution by the underlying stellar background. This leads to a radial anticorrelation between EW(Hα) and stellar surface density, similar to the case of the local BCD I Zw 18 (Papaderos et al. 2002, and PO12), as delineated in the right-hand panel.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


