Fig. 8
Download original image
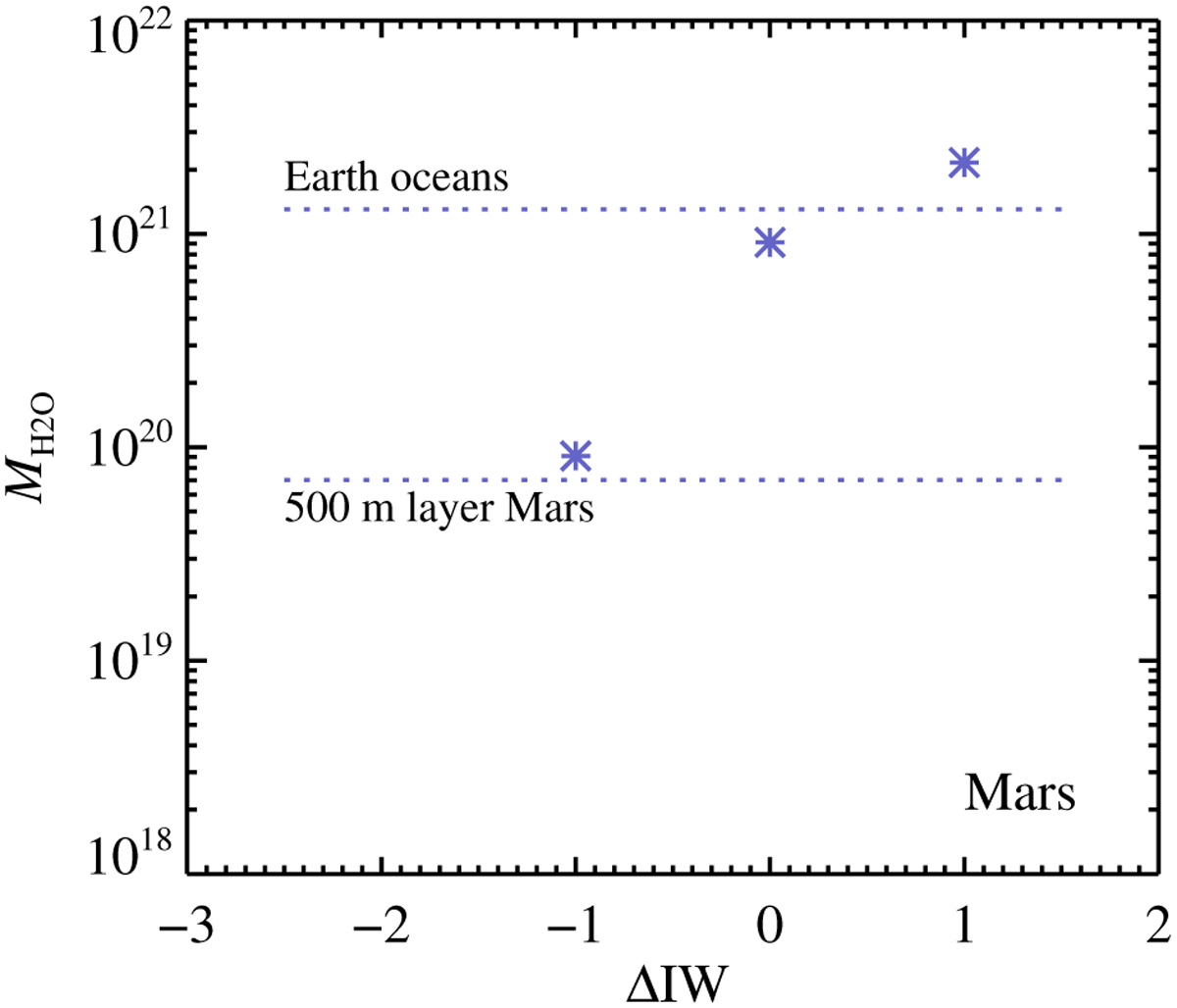
Mass of water in the surface reservoir of Mars (condensed and vapour) as a function of the oxidation state of the mantle relative to the iron–wüstite buffer (IW), with higher values of ΔIW indicating increasing partial pressure of oxygen in the atmosphere. The top line marks the modern Earth ocean mass, while the bottom line marks a 500 metre water layer on Mars. For the nominal value of ΔIW – 2, Mars loses its entire surface and atmosphere water reservoir, but the water amount increases rapidly from IW-1 and upwards.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


