Fig. 5.
Download original image
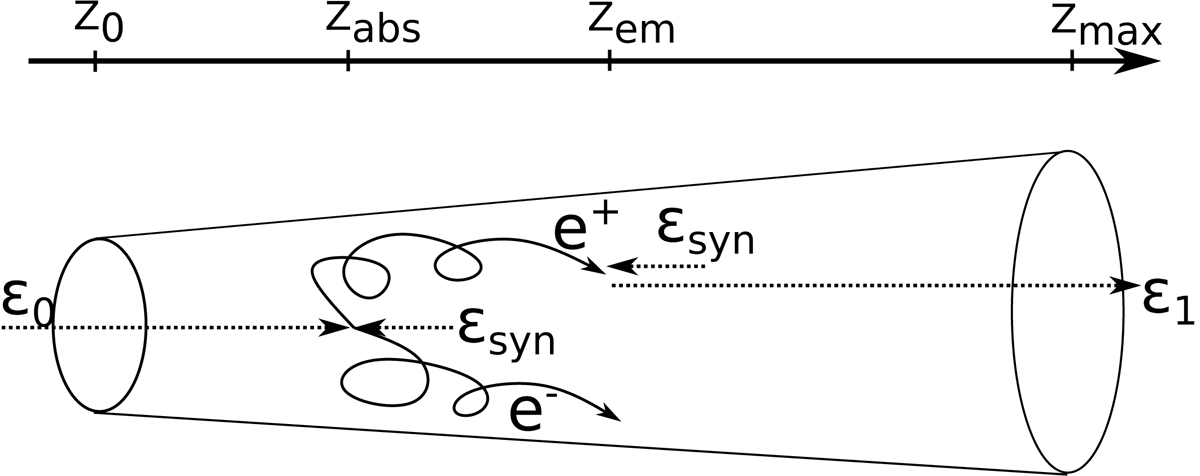
Schematic picture of the IC e± cascade that develops within the jet volume (not to scale). The primary γ-ray photon, ϵ0, is injected at the jet base located at z0. The photon is absorbed in the synchrotron radiation of the inhomogeneous jet. The secondary e± pair is created as a result of the absorption at a distance zabs. This e± pair is isotropized in the random component of the magnetic field of the jet. It is rather advected with the jet plasma. The e± pair is cooled down, producing synchrotron radiation and secondary γ-ray photons in the IC process. These secondary photons, ϵ1, created at a distance zem, can be also absorbed or escape from the jet.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


