Fig. 3.
Download original image
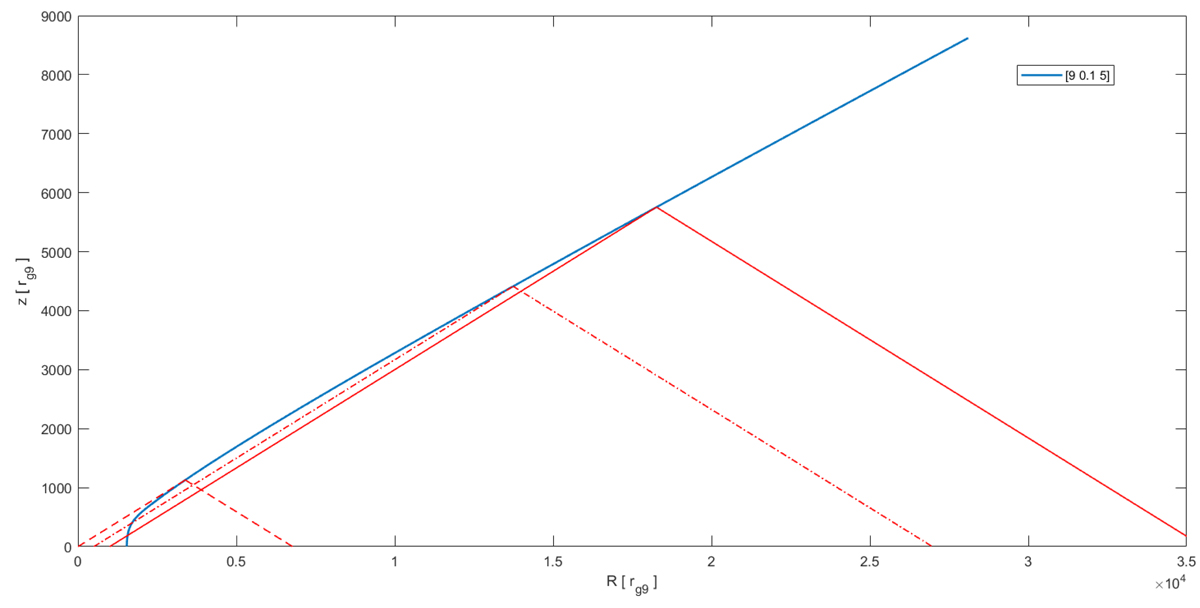
Illustration of the shielding effect in our model. Here, we show the radial extension of the disk area seen by the selected flying cloud at three different exemplary positions along its trajectory, for the case of escaping cloud launched at 1540 rg with black hole mass of 109 M⊙, Eddington rate of 0.1, and five times solar metallicity. The cloud located at vertical position of around 1100, 4500, and 5800 rg along its trajectory, sees the radial range of [0–6700], [500–26 800], and [1000–35 600] rg, respectively. The model assumes the radial visibility as three times higher than the local cloud height (α = 3, see Naddaf et al. 2021), so the area at the starting point is very small and we cannot show the early stages in this graphical scale, but the cloud is well exposed to the whole disk irradiation after reaching the height of 1000 rg. Other clouds may never achieve such exposure to the disk central parts.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


