Fig. 7
Download original image
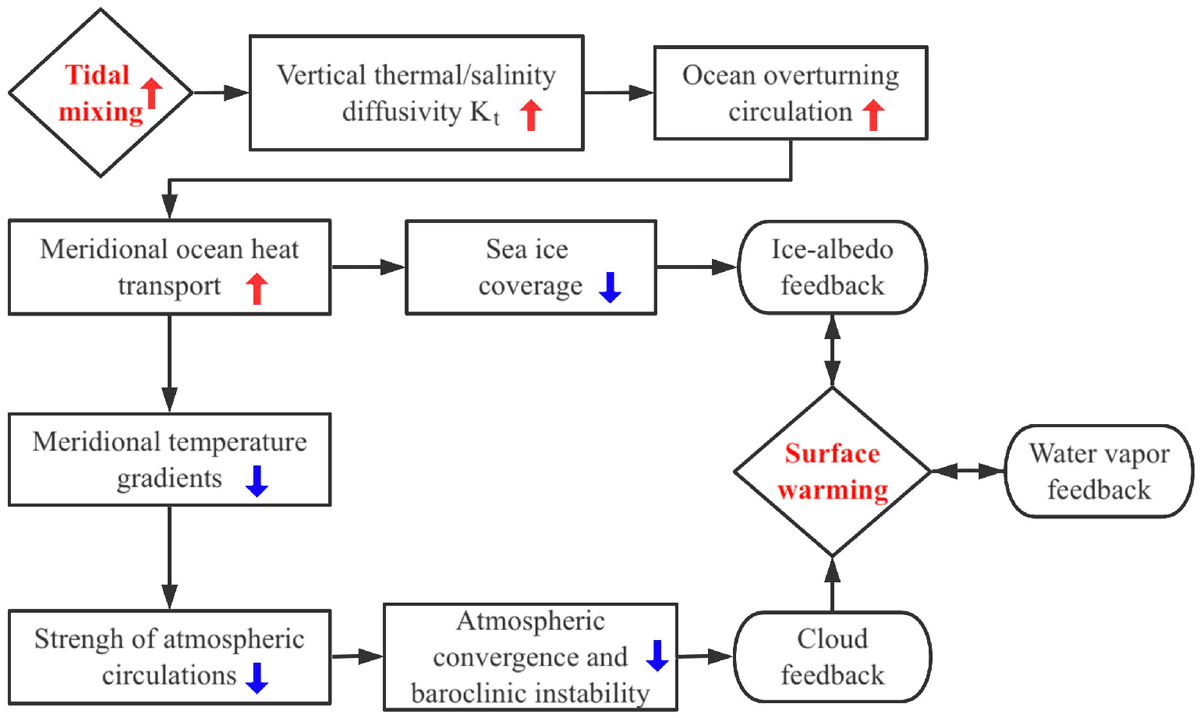
Schematic showing how stronger tidal mixing leads to global surface warming. The stronger tidal mixing enhances the oceanic MOC and thereby the meridional ocean heat transport. As a result, the polar sea ice coverage decreases, and the ice-albedo feedback warms the surface. The stronger ocean heat transport also decreases the meridional temperature gradient and weakens the atmospheric convergence and baroclinic instability of the atmosphere, and the cloud feedback further warms the surface. In addition, water vapor feedback also acts to warm the planetary surface.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


