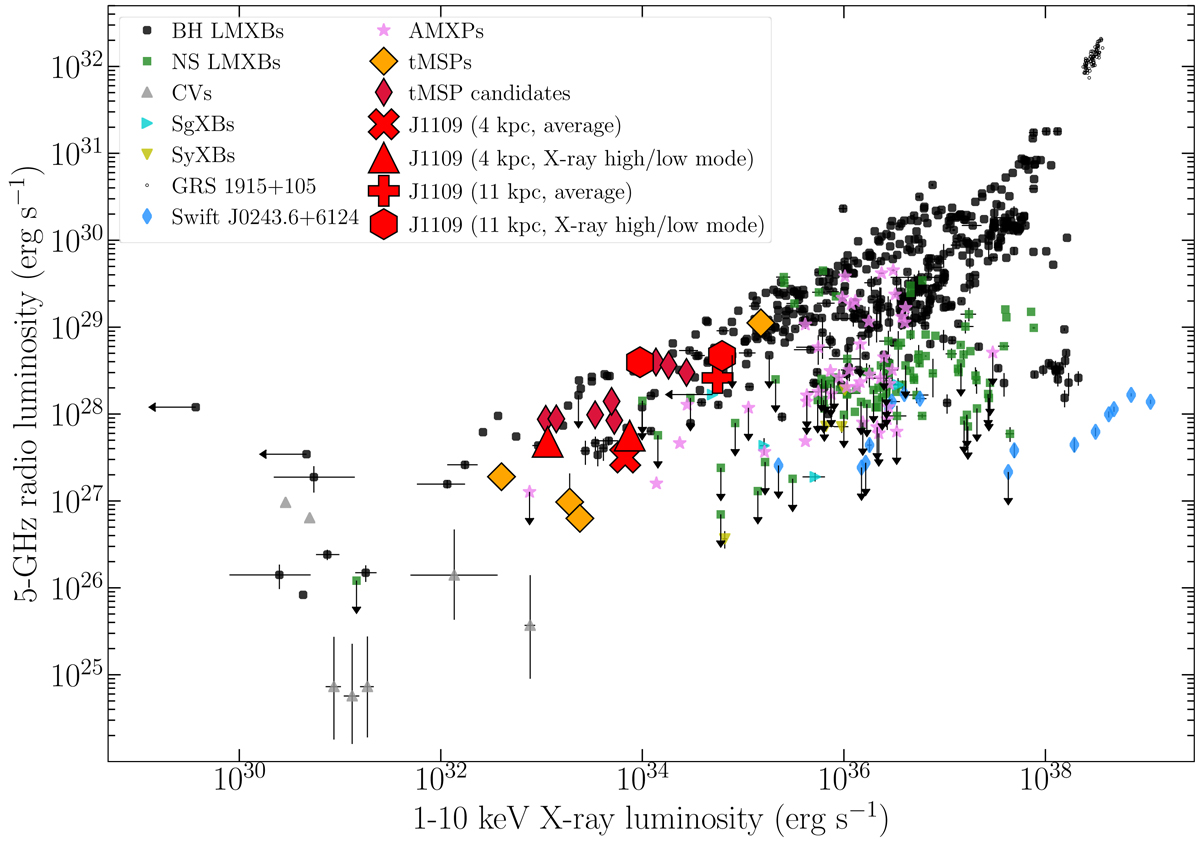
Fig. 4.
Download original image
Radio and X-ray luminosities for different classes of binary systems harbouring different types of accreting compact objects, including low-mass X-ray binaries with BHs and NSs accretors (BH LMXBs, NS LMXBs), cataclysmic variables (CVs), supergiant X-ray binaries (SgXBs), symbiotic X-ray binaries (SyXBs), the peculiar Be X-ray binary Swift J0243+6124, accreting millisecond X-ray pulsars (AMXPs) and known and candidate tMSPs in the disk state. Values are derived from simultaneous or quasi-simultaneous (within 1−2 d) radio and X-ray observations, and are taken from Bahramian et al. (2018) with updates from Bassi et al. (2019), Coti Zelati et al. (2019), Gusinskaia (2019), Parikh et al. (2019), Bright et al. (2020), Gusinskaia et al. (2020a,b), Hewitt et al. (2020), Li et al. (2020), Tremou et al. (2020), Williams et al. (2020), Xie et al. (2020), van den Eijnden et al. (2020, 2021), de Haas et al. (2021), Carotenuto et al. (2021), Motta et al. (2021), Paduano et al. (2021). Values for J1109 are plotted separately for the averaged emission and for the emission during the high and low X-ray modes. Error bars on data points (when available) indicate 1σ uncertainties, and are smaller than the marker size for most of the data points (including those corresponding to J1109). Upper limits are marked using arrows.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


