Fig. 1
Download original image
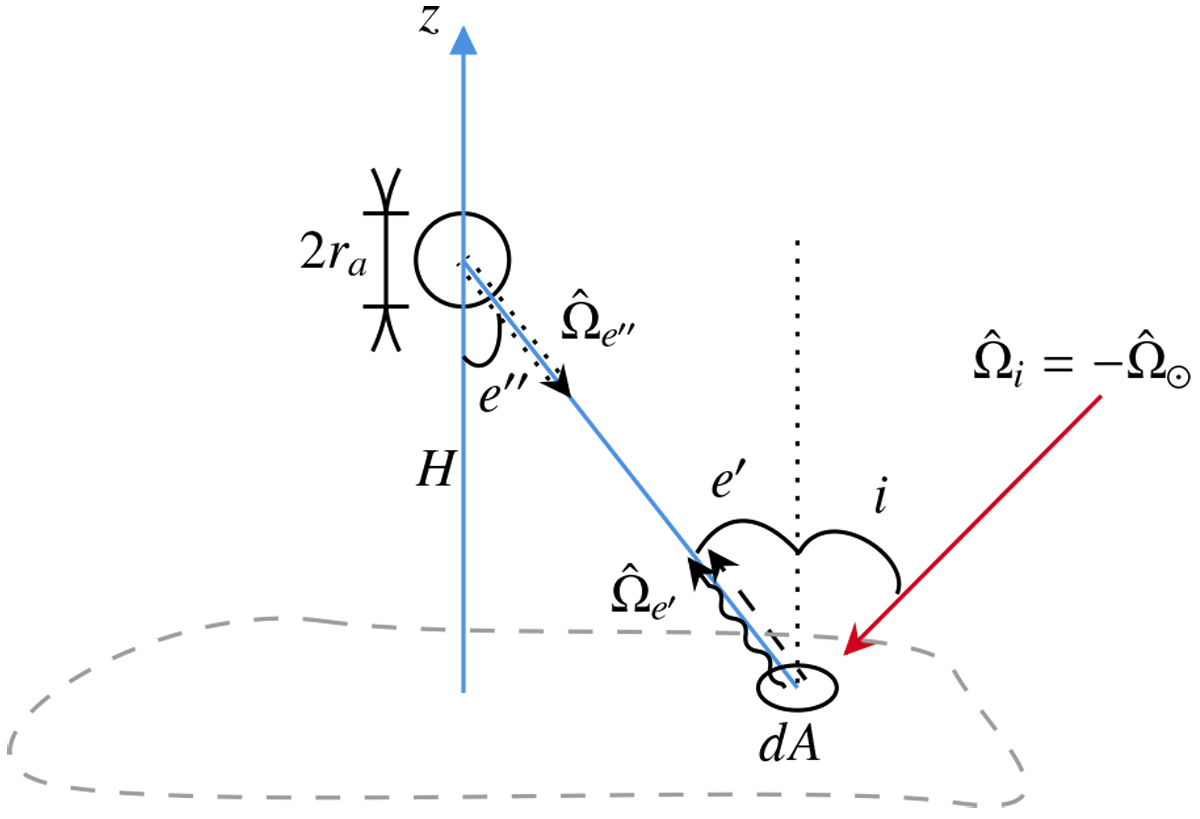
Schematic diagram of a spherical particle hovering over the surface. The particle of radius ra hovers over the planar regolith at the height of H(≫ ra). The solar irradiation (the long red arrow) is originated from the direction ![]() . A tiny surface patch with an area of dA reflects the solar radiation and emits the thermal radiation to the particle (the dashed and squiggly arrows, respectively, to the directionof
. A tiny surface patch with an area of dA reflects the solar radiation and emits the thermal radiation to the particle (the dashed and squiggly arrows, respectively, to the directionof ![]() ) with the emission angle of e′. In our model, e″ = e′ holds because of the planar surface assumption. The isothermal regolith region (gray dashed) is assumed to be a circle with a radius of r0(≫ H ≫ ra). No radiation outside this region is considered because the patch right below the particle already fills most of the field of view (r0 ≫ H).
) with the emission angle of e′. In our model, e″ = e′ holds because of the planar surface assumption. The isothermal regolith region (gray dashed) is assumed to be a circle with a radius of r0(≫ H ≫ ra). No radiation outside this region is considered because the patch right below the particle already fills most of the field of view (r0 ≫ H).
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


