Fig. 7.
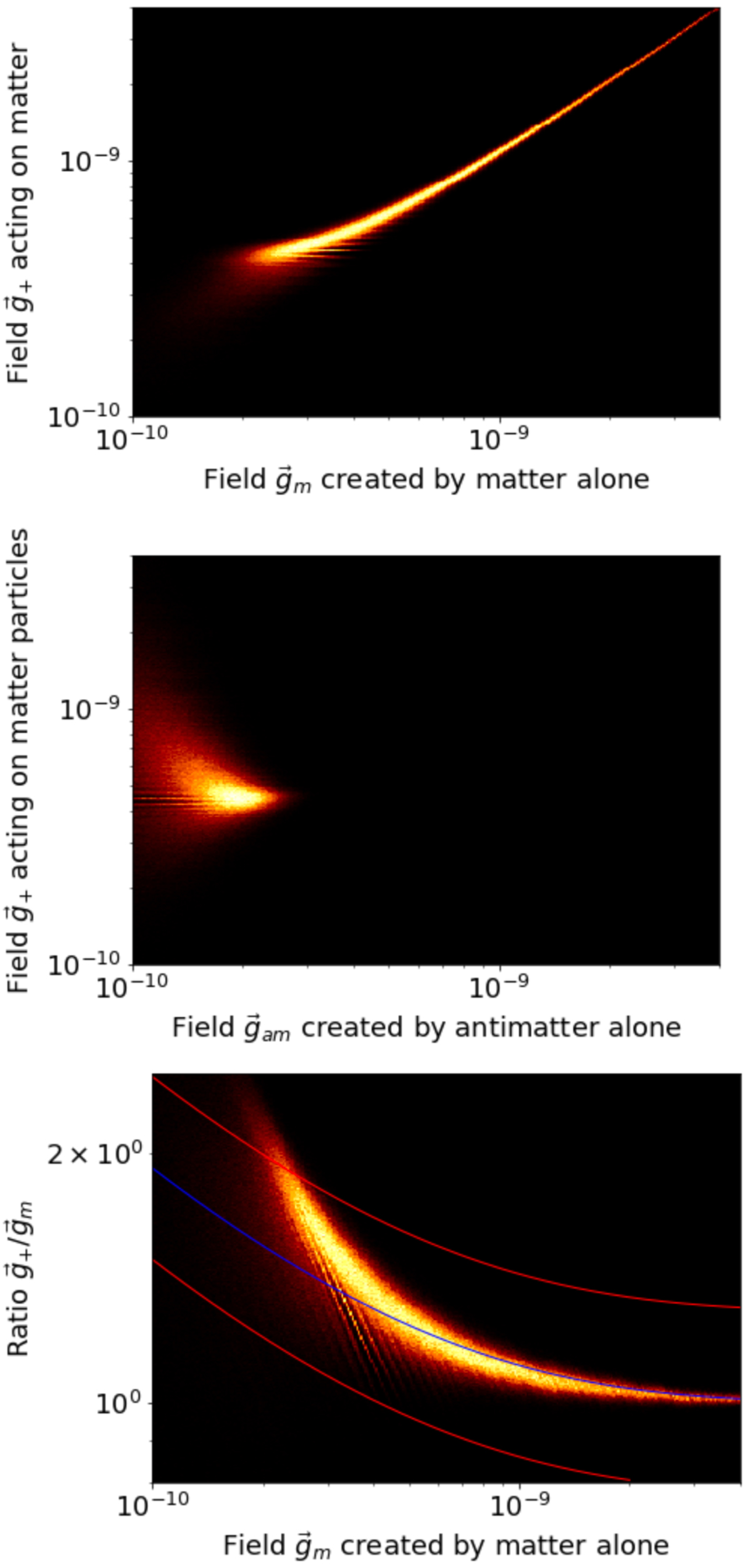
Top panel: total gravitational field acting on a matter particle as a function of the gravitational field created by matter alone. A Newtonian regime can be observed for the high field region of the figure, with a gradual transition from the Newtonian regime to a MOND-like regime at an acceleration of ≈1.0 × 10−9 m s−2. Middle panel: total gravitational field acting on a matter particle as a function of the gravitational field created by antimatter alone. The antimatter field is rather peaked, with an average value of ≈2 × 10−10 m s−2. Bottom panel: ratio between the total gravitational field acting on a matter particle and the Newtonian field (created by matter only), as a function of the gravitational field created by matter only. Almost exactly unity in the Newtonian regime (at high values of the field), this ratio gradually increases and reaches a factor of ≈2 at the end of the depletion zone. The MOND interpolating function used in Lelli et al. (2019) for a value of the a0 parameter 1.85 × 10−10 m s−2 has been superimposed on the simulation data, while the two adjacent curves represent the 1-σ error of 0.11 dex found by these authors.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


