Fig. 2
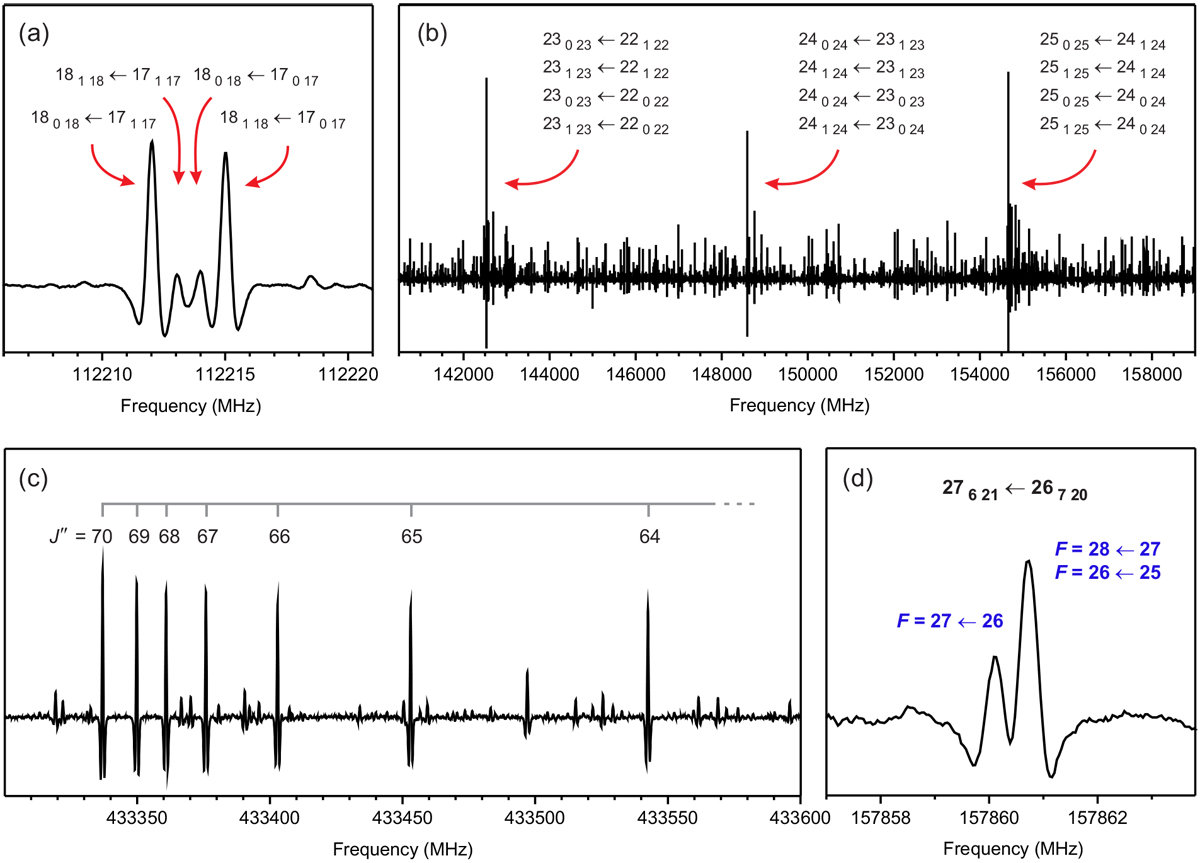
Illustrations of the main characteristics of the room-temperature rotational spectrum of propiolamide. (a) An example of a quartet of a-type and b-type R-branch rotational transitions between Ka = 0, 1, Kc = J pairs of energy levels. (b) Quadruply degenerate lines consisting of a pair of a-type and a pair of b-type transitions involving the same Ka = 0, 1 pairs of levels. These strong lines appear in the spectrum approximately every 6.06 GHz, which corresponds to the value of 2C. (c) An example of a group of high-J quadruply degenerate transitions. The leading transition is J = 71 ← 70 and the value of J decreases by 1 with each successive line running to higher frequencies. The Ka quantum number is increasing away from the leading line in such a way that the first line corresponds to four degenerate Ka = 0, 1 transitions, the second to Ka = 1, 2, the third to Ka = 2, 3, and so on. (d) An example of 14N nuclear quadrupole hyperfine structure observed in the millimeter wave spectrum. The F = J ± 1 hyperfine components typically appear overlapped, while the F = J component is, in many cases, relatively well separated.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


