Fig. 11.
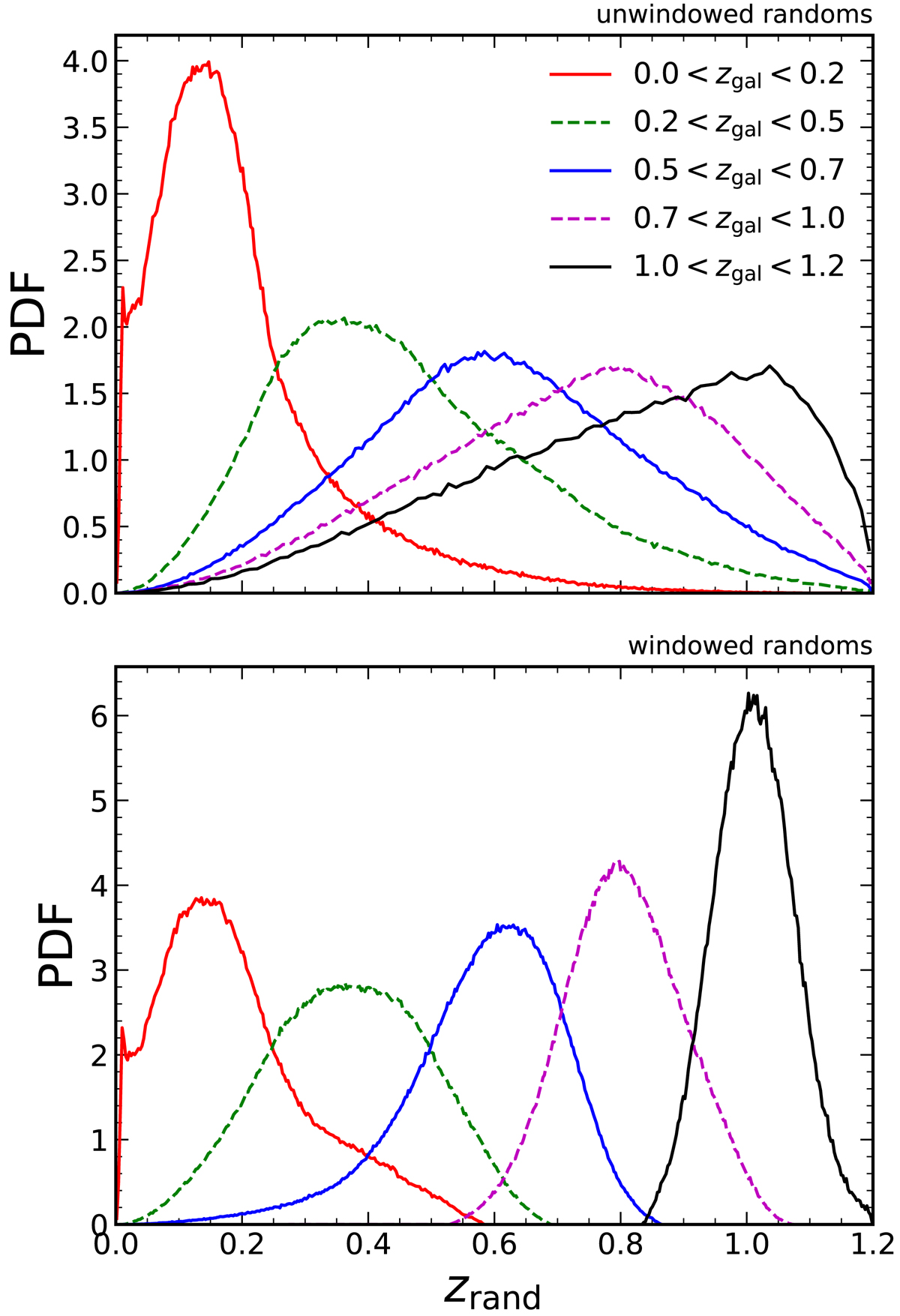
Redshift distributions of random clones zrand, whose parent galaxies are situated at photometric redshifts zgal. Top: unwindowed clones are scattered over the entire redshift range, depending on the brightness, and hence zmax, of parent galaxies. Bottom: for the windowed randoms, 71.5% of a galaxy’s random clones are scattered within a ±1σ symmetric volume, centred on the location of the parent galaxy [we display σ = 3 × 106 (h−1 Mpc)3 randoms here, for a clearer illustration]. We note that the symmetry is in volume coordinates, hence in redshift/comoving coordinates the windows are extended in the direction of the observer, and slightly squashed in the outward direction. This figure is closely based on a similar plot presented by Farrow et al. (2015) for GAMA galaxies and randoms (their Fig. 3). Plateaus in the red curves, on approach to redshift zero, correspond to faint, very low-redshift galaxies which are excluded from our analysis.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


