Fig. 7.
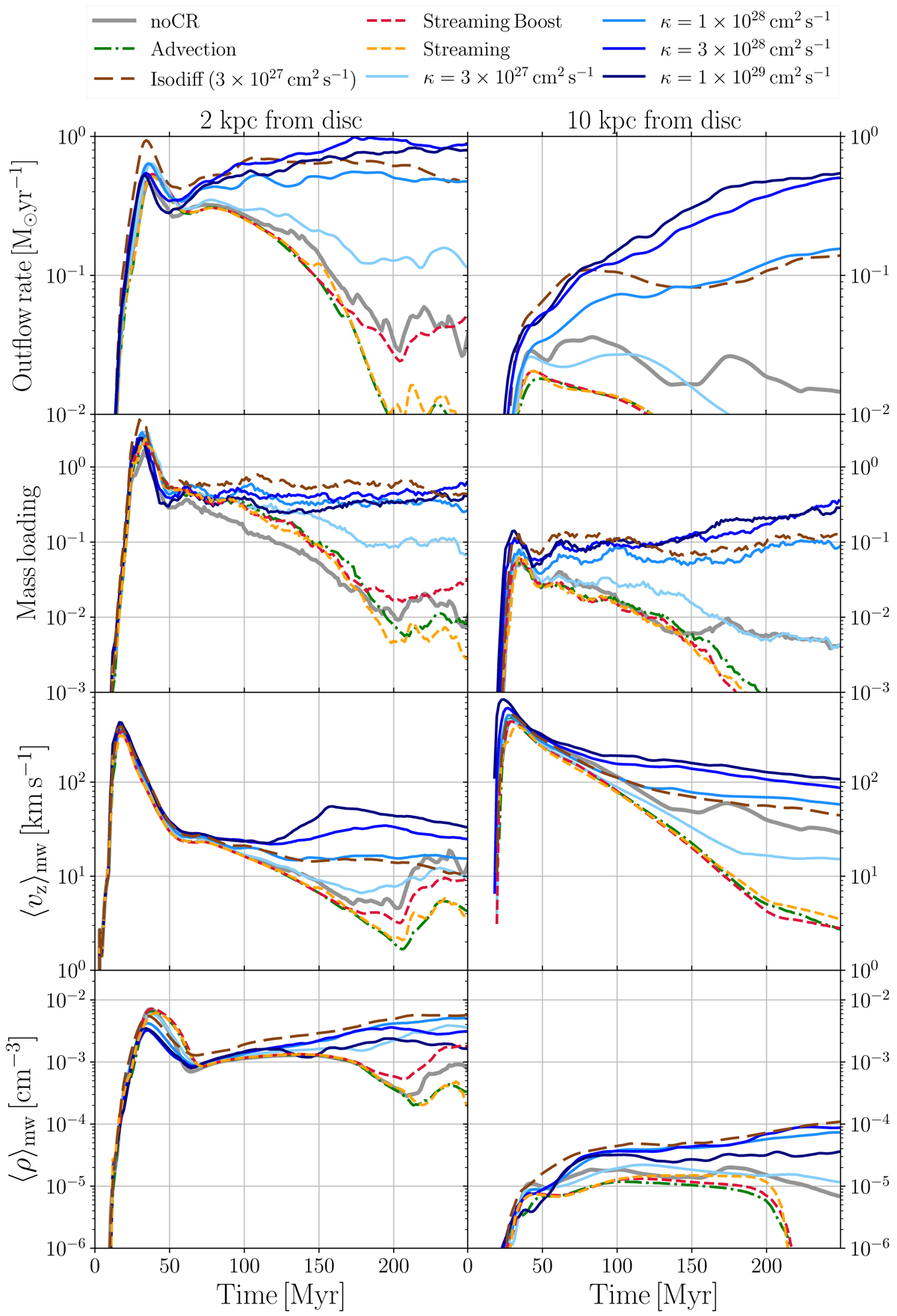
Mass outflow rates of the outflowing gas, mass loading factors, mass-weighted average velocities and mass-weighted average density of the outflowing gas across planes at 2 (left column) and 10 kpc (right column) above the disc plane of the G9 galaxy. The outflow rate quickly drops without CR injection and transport, in the noCR and Advection models. In the Advection-only model, the lack of CR transport prevents the generation of sustained outflows. The outflow rate in the Streaming Boost simulation is very similar to the Advection case at early times and rises to higher values at later times, but the outflow rate is sill weaker than with the other transport models. The isotropic diffusion model and anisotropic diffusion with κ = 3 × 1028 − 1 × 1029 cm2 s−1 are more than 10 times more efficient at driving winds compared to the noCR case. The mass average outflow velocity is less affected by the injection of CRs: it is increased at most by a factor of 2 for the highest diffusion coefficient, and is even lower for κ = 3 × 1027 cm2 s−1.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


