Fig. 6
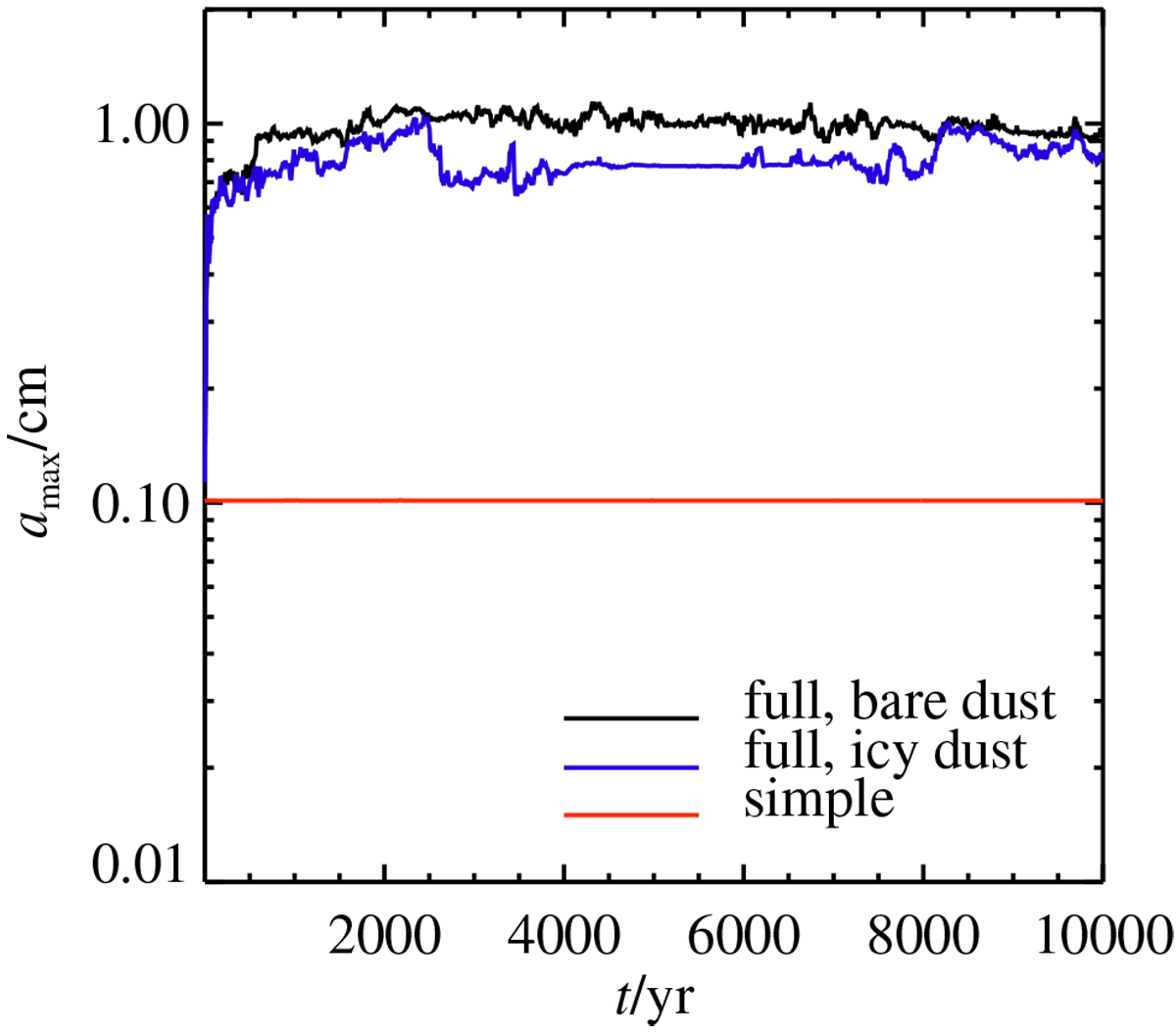
Comparison of particle growth in the full temperature-dependent nucleation model and in the simple model, when including both micrometre-sized silicate grains and millimetre-sized ice-covered pebbles. In the simple model, shown in red, we ignore the difference between the critical saturation ratios needed for heterogeneous nucleation and vapour deposition. Vapour is then deposited on the micrometre-sized dust grains where most of the surface area resides, and the millimetre-sized particles do not grow. In the full nucleation model, denoted by a black line for initially bare dust and a blue line for initially ice-covered dust, heterogeneous ice nucleation of vapour on bare silicate particles is not possible, as the supersaturation required for heterogeneous nucleation is never reached. As a result, the icy pebbles grow quickly from millimetre to centimetre sizes.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


