Fig. 7.
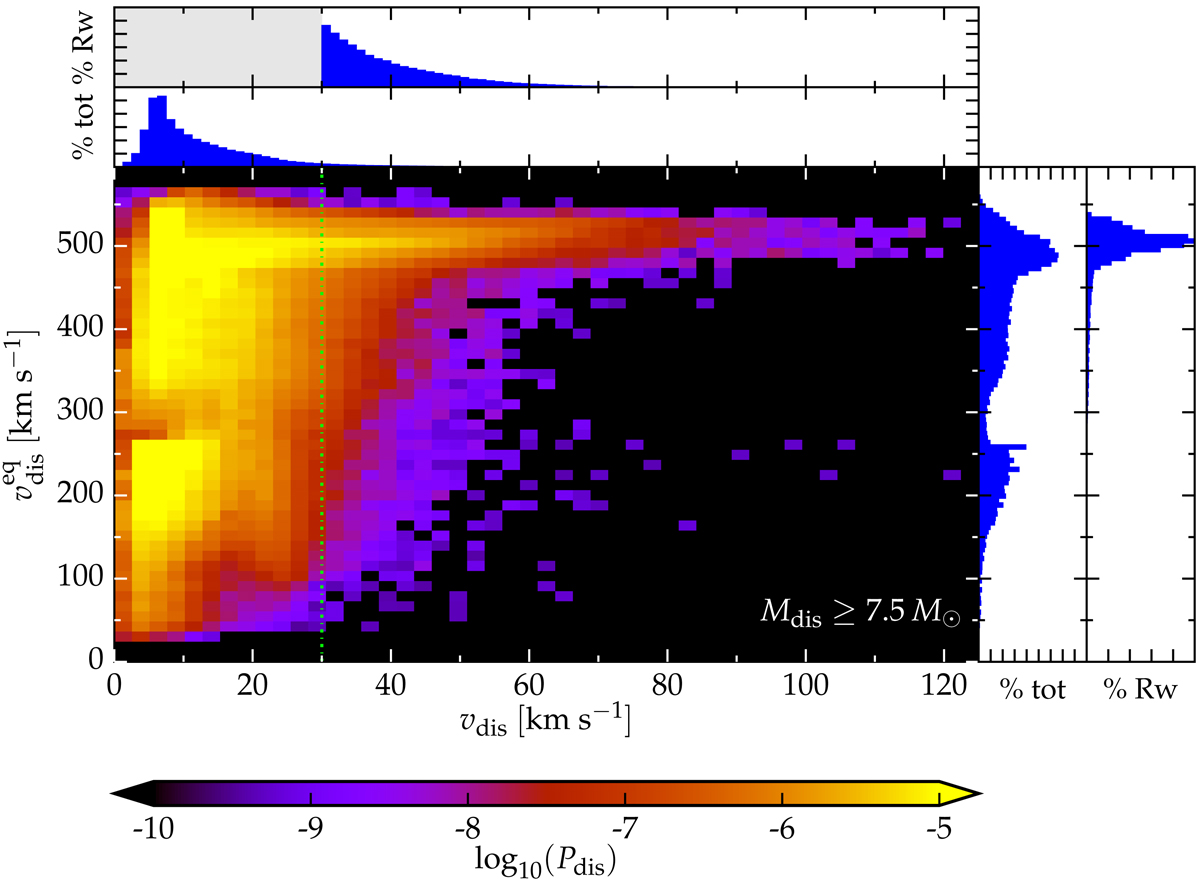
Equatorial velocity at the time of ejection for massive (Mdis ≥ 7.5 M⊙) companions as a function of the ejection velocity. Brighter colors indicate location of the parameter space more populated by our fiducial simulation. All the massive runaway stars spin with an equatorial velocity of ∼500 km s−1, close to breakup rotation, since they have accreted mass from their companion before being ejected. The spread is due to wind spin down before the binary disruption. We do not include the effect of projecting on the line of sight, or post-ejection wind spin down in this plot. The vertical dot-dashed line marks the threshold to define runaway stars.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


