Fig. 1.
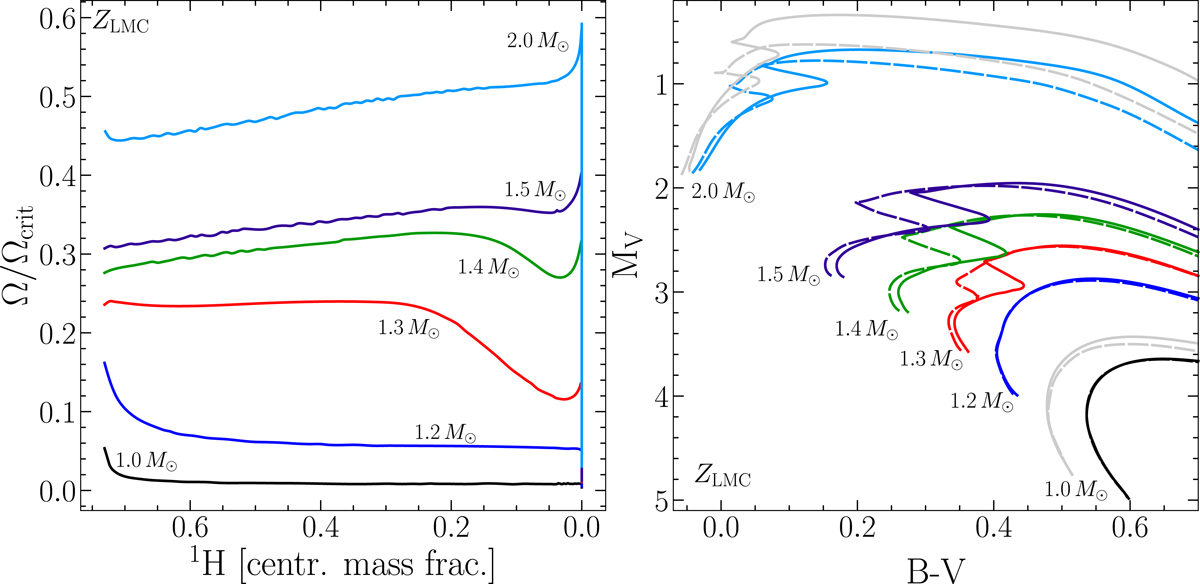
Left panel: evolution of the ratio of the surface angular velocity to the critical velocity for STAREVOL models with [Fe/H] = −0.3 relevant for LMC metallicity (this corresponds to a metal mass fraction Z = 0.008 for the adopted initial chemical mixture). Central hydrogen mass fraction (in abscissa) is a proxy for time evolution along the MS (left to right). For each mass (colour-labelled), model predictions are shown for the median rotators of the grid of Amard et al. (in prep.). The transition is clearly visible between models that are braked early on the MS by the coupling of the surface magnetic field and the stellar winds (≤1.2 M⊙), and models that are never braked (≥1.5 M⊙). Right panel: evolution tracks in the CMD for stellar models of different masses (see label near the tracks, the colour code for the STAREVOL models is the same as in left panel), at the metallicity of the LMC. Standard models (no rotation, dashed lines) are compared with the rotating models (solid lines). For comparison purposes, we also indicate the tracks of 1 M⊙ and 2 M⊙ models computed with the Geneva code (GENEC), shown in grey (Eggenberger et al., in prep., same physics as in Ekström et al. 2012) at a metallicity Z = 0.006, corresponding to [Fe/H] = −0.376. The metallicity and initial mixture of the two sets of models are not exactly the same, explaining the slight shift of the tracks from the ZAMS on.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


