Fig. 4.
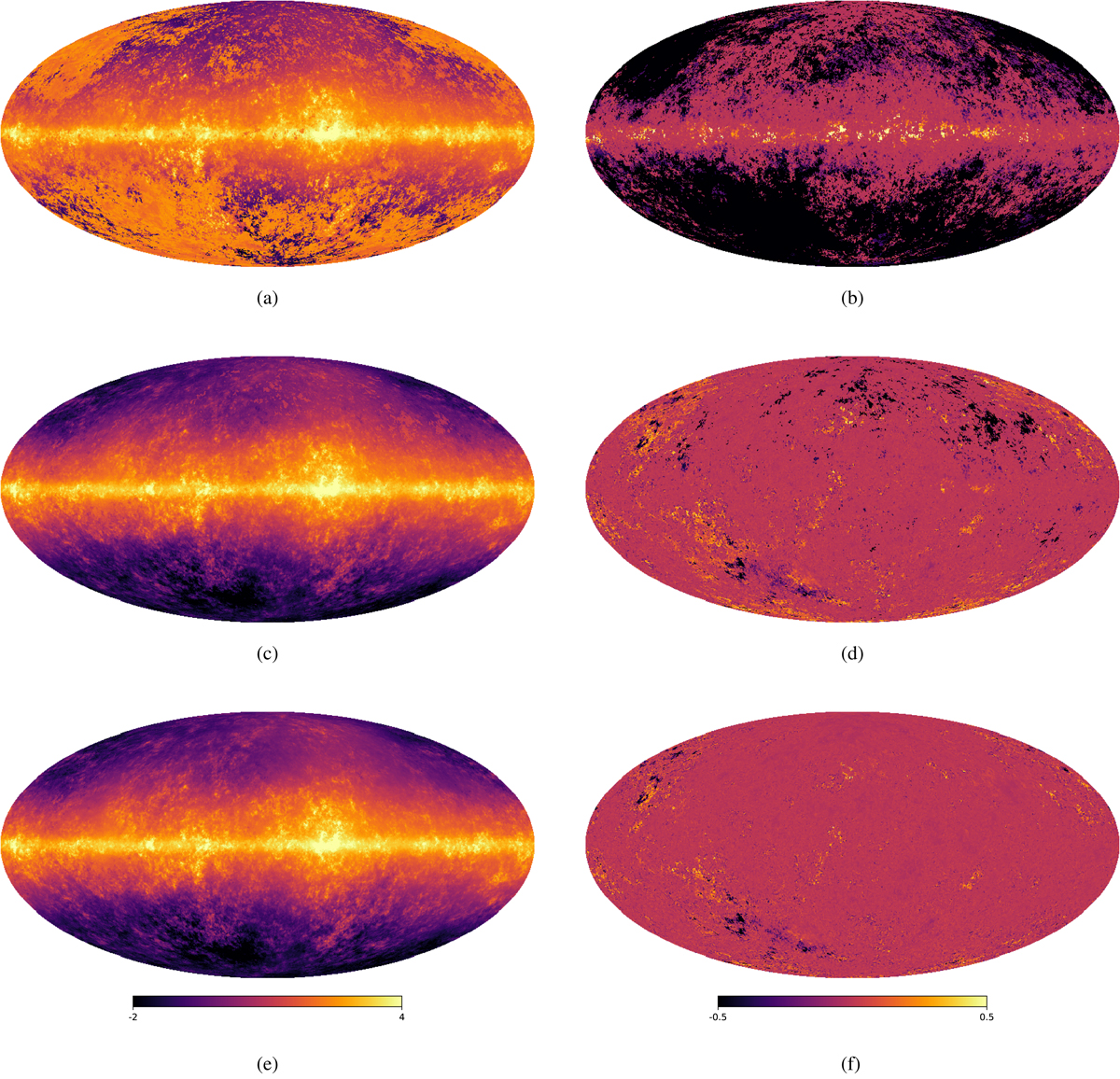
Simulation of the restoration of unobserved areas. The GMM is trained with K = 9 Gaussians using different observed parts of the whole sky from Mock I and the full maps of Mock II--VI. The predictions are determined from the CPD marginalized over the respective partial maps of Mock I. Panel a: prediction of Mock I with only the disk information as GMM input. Panel b: difference between the original Mock I map and the prediction computed from only the disk information, rms = 1.64. Panel c: prediction of Mock I with the disk and only a small part of the southern hemisphere information as GMM input. Panel d: difference between the original Mock I map and the prediction computed from the disk and a small part of the southern hemisphere background information, rms = 0.14. Panel e: prediction of Mock I with only the southern hemisphere information as GMM input. Panel f: difference between the original Mock I map and the prediction computed from the southern hemisphere information, rms = 0.07.
Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.


